Real-time tracking and prediction of RNA virus evolution
Richard Neher
Biozentrum, University of Basel
slides at neherlab.org/201710_ASMNGS.html
Human seasonal influenza viruses
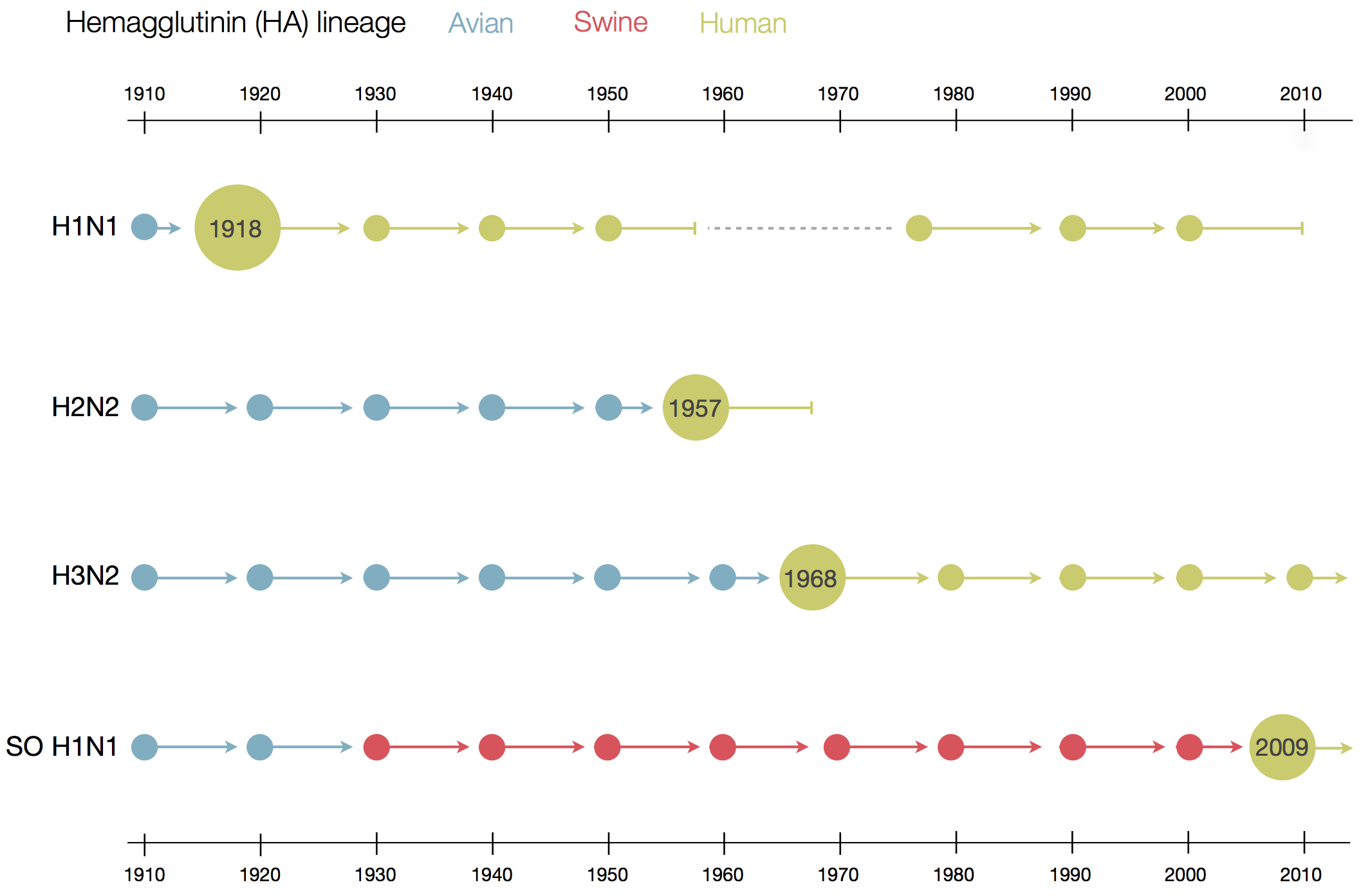
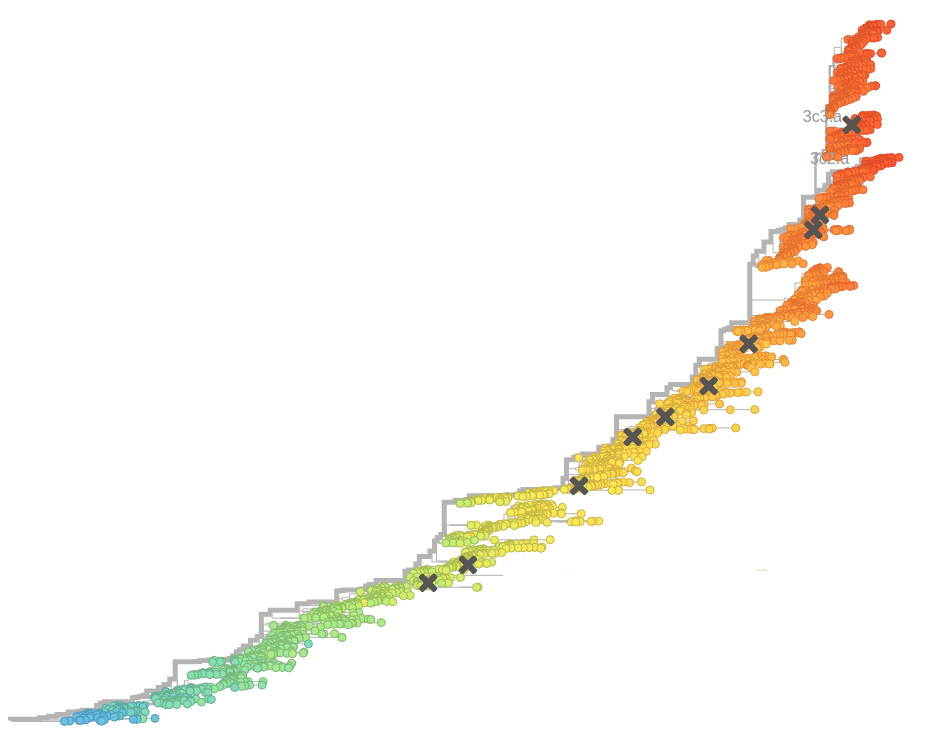
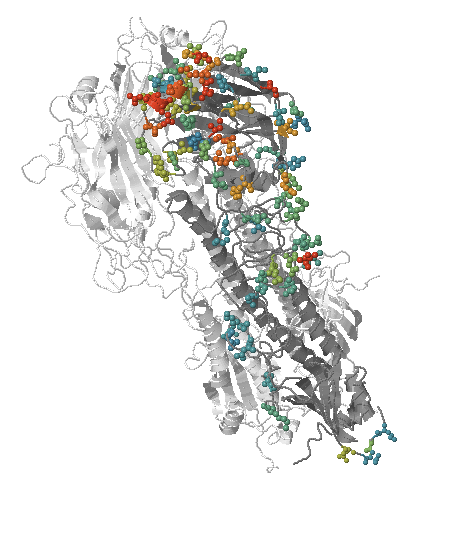
- Influenza viruses evolve to avoid human immunity
- Vaccines need frequent updates
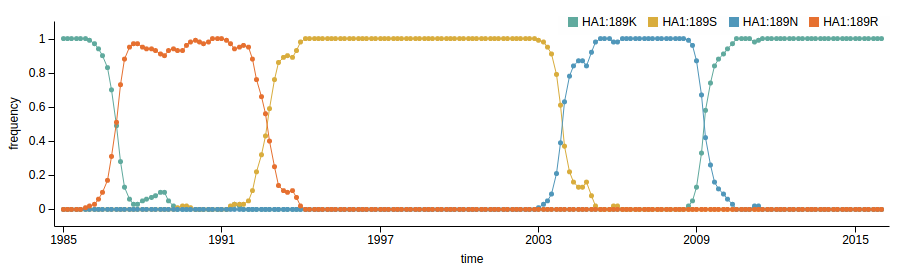
nextflu.org
joint work with Trevor Bedford & his lab
code at github.com/blab/nextflu
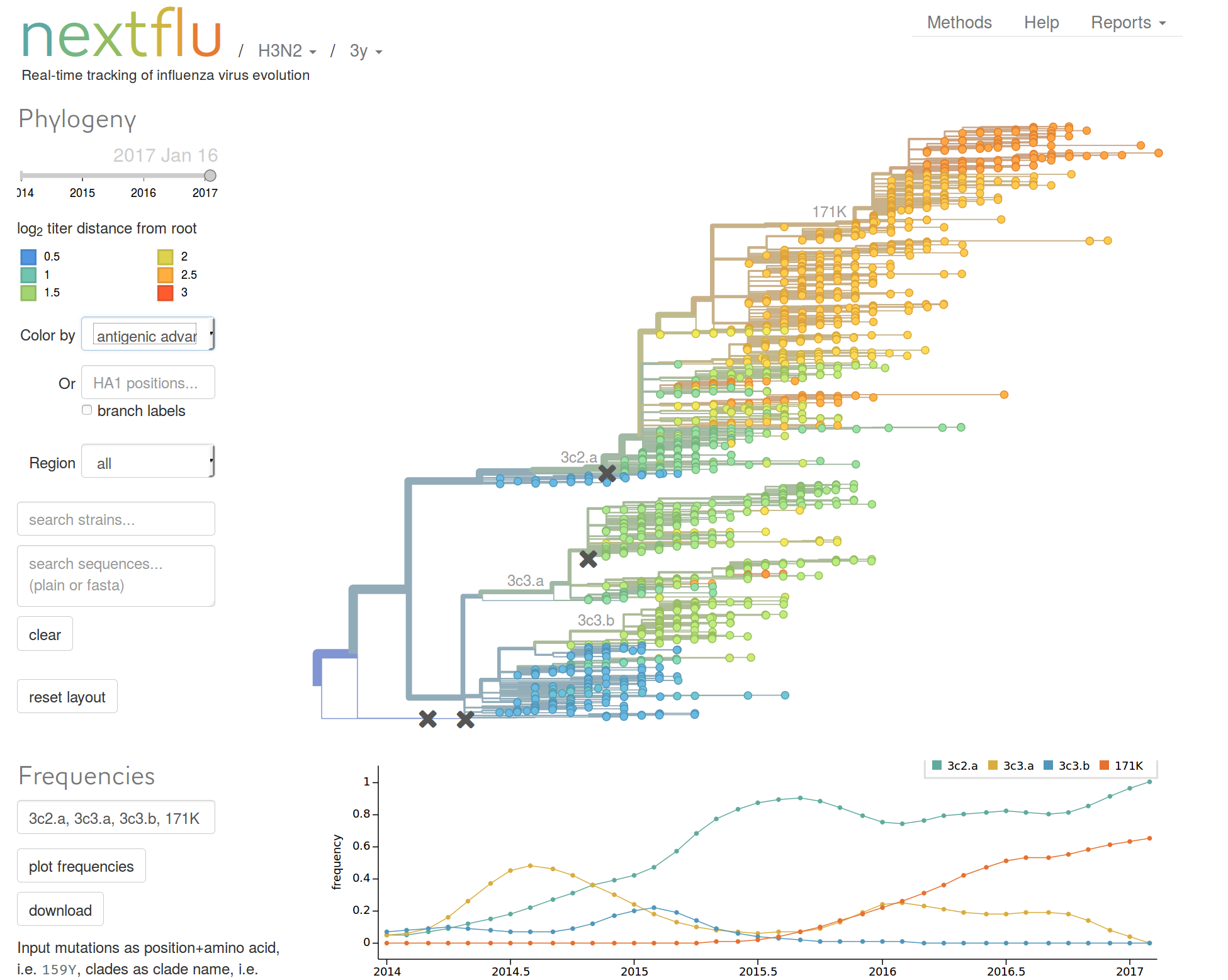
Beyond tracking: can we predict?
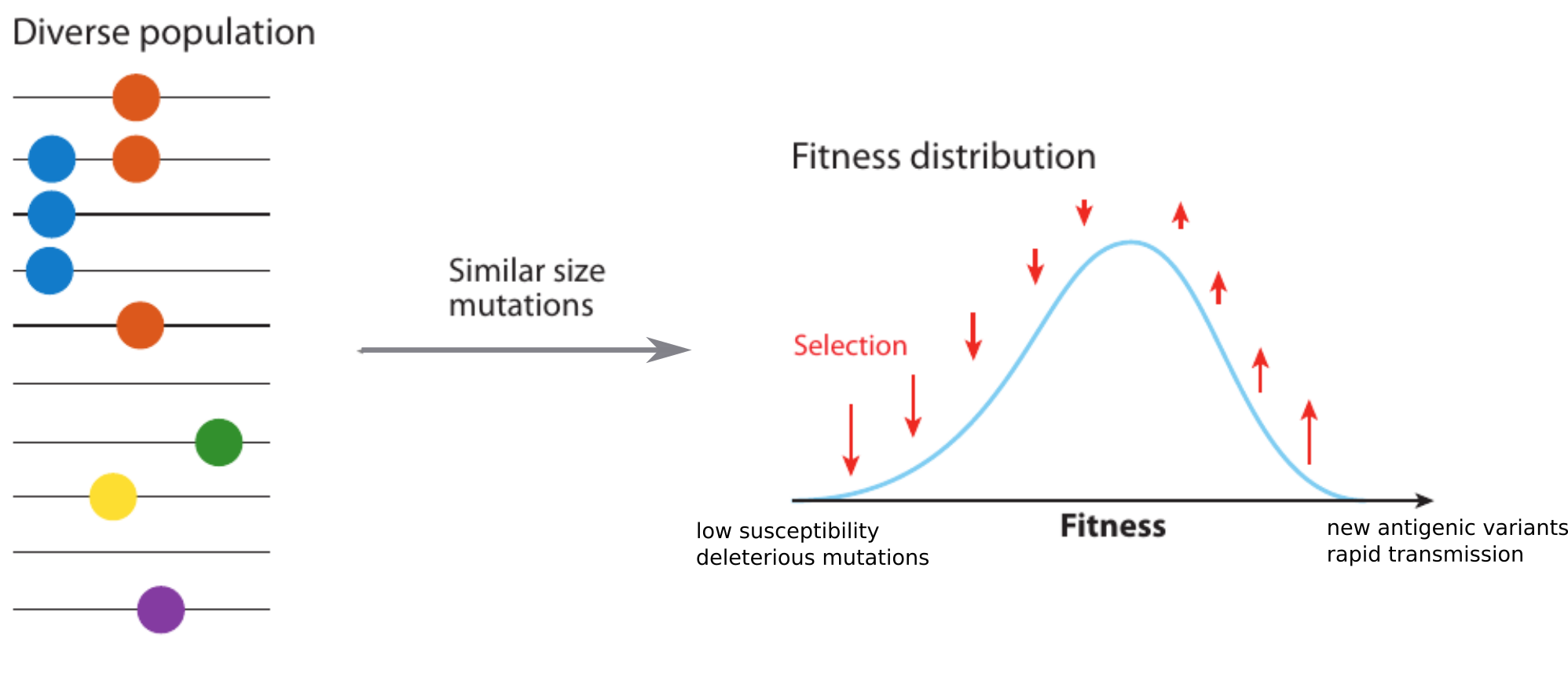
Model of rapidly adapting virus populations
Typical tree
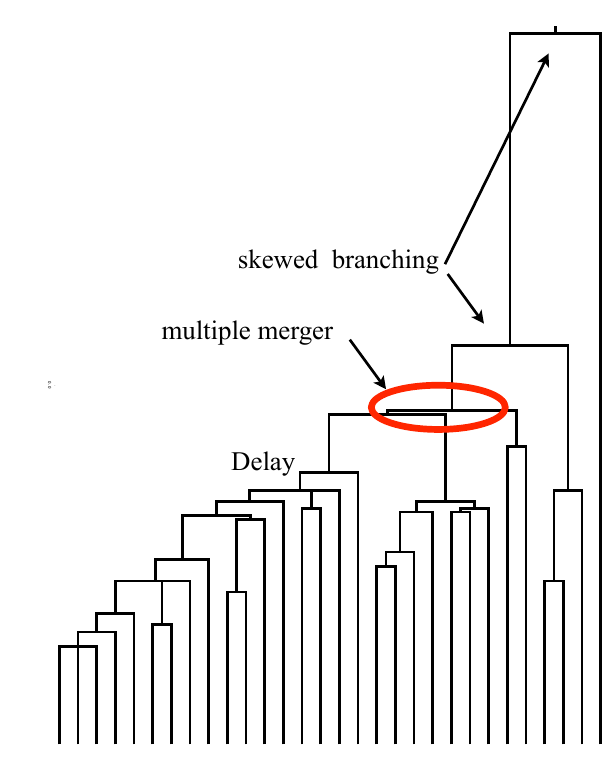
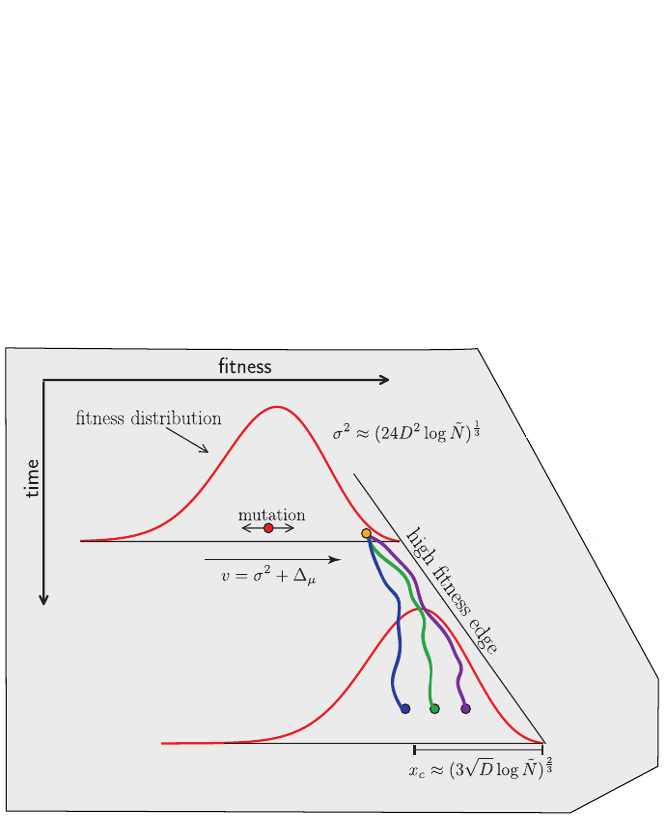
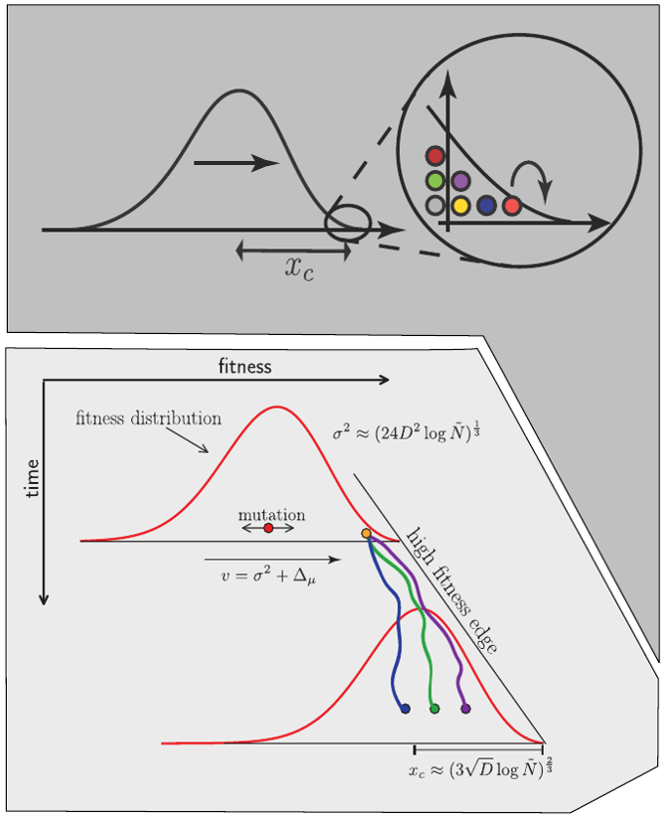
Bolthausen-Sznitman Coalescent
Bursts in a tree ↔ high fitness genotypes
Predicting evolution
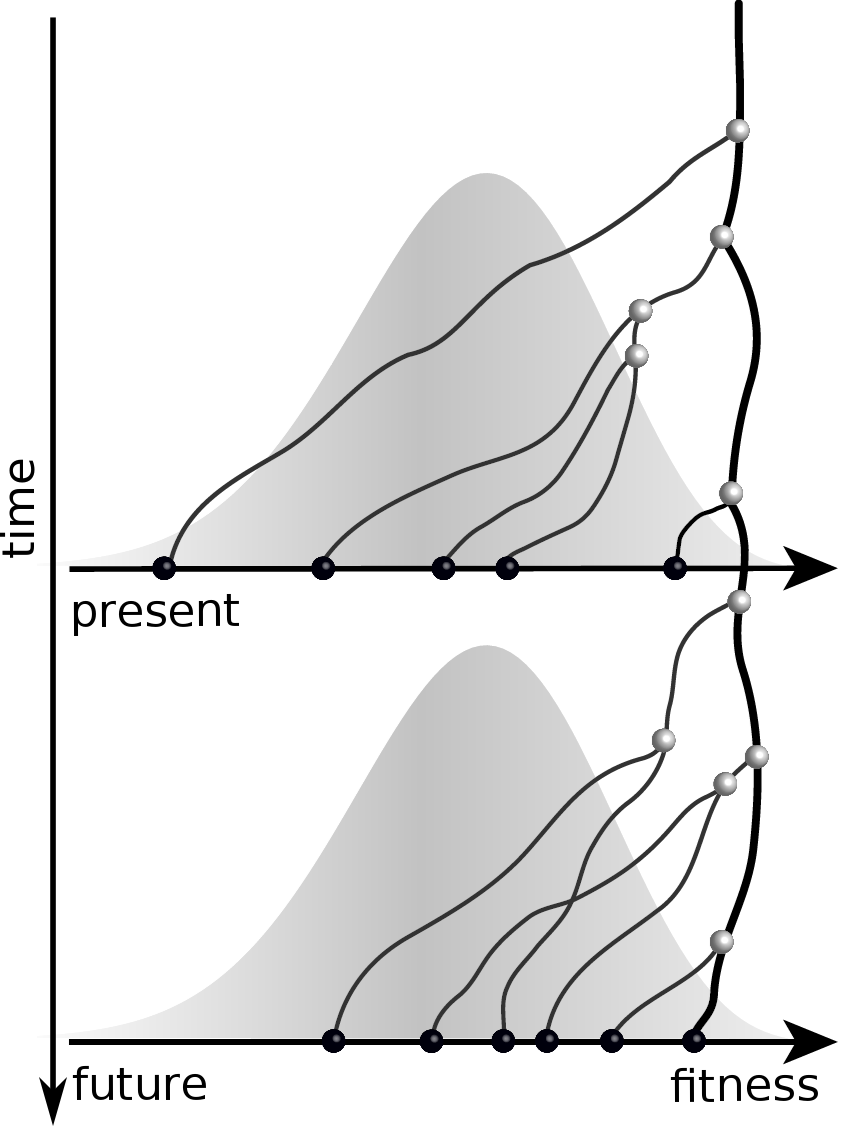
Given the branching pattern:
- can we predict fitness?
- pick the closest relative of the future?
Fitness inference from trees
$$P(\mathbf{x}|T) = \frac{1}{Z(T)} p_0(x_0) \prod_{i=0}^{n_{int}} g(x_{i_1}, t_{i_1}| x_i, t_i)g(x_{i_2}, t_{i_2}| x_i, t_i)$$
RN, Russell, Shraiman, eLife, 2014
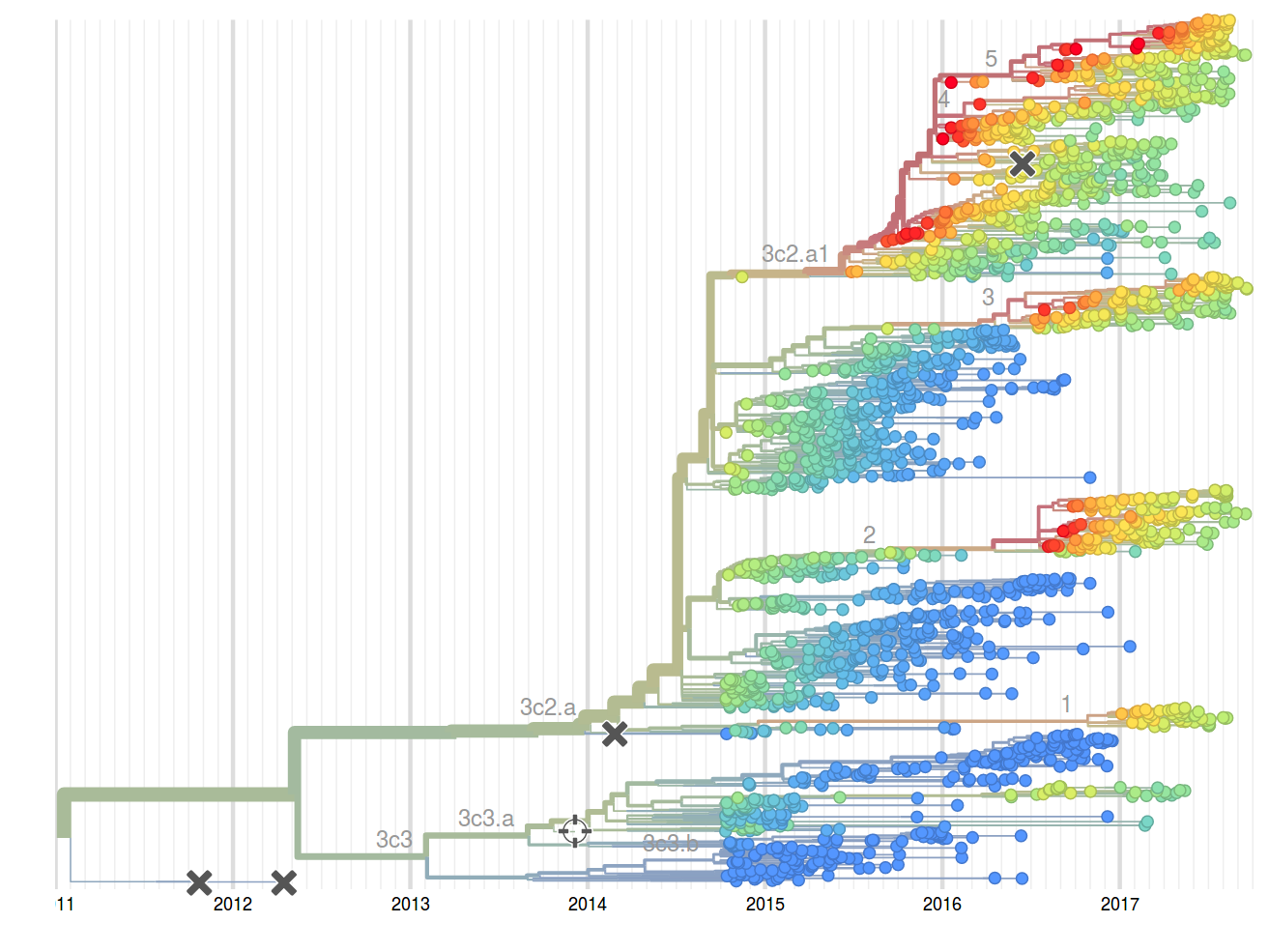
Prediction of the dominating H3N2 influenza strain
- no influenza specific input
- how can the model be improved? (see model by Luksza & Laessig)
- what other context might this apply?
Prediction of the dominating H3N2 influenza strain
nextstrain.org
joint work with Trevor Bedford & his lab
code at github.com/nextstrain
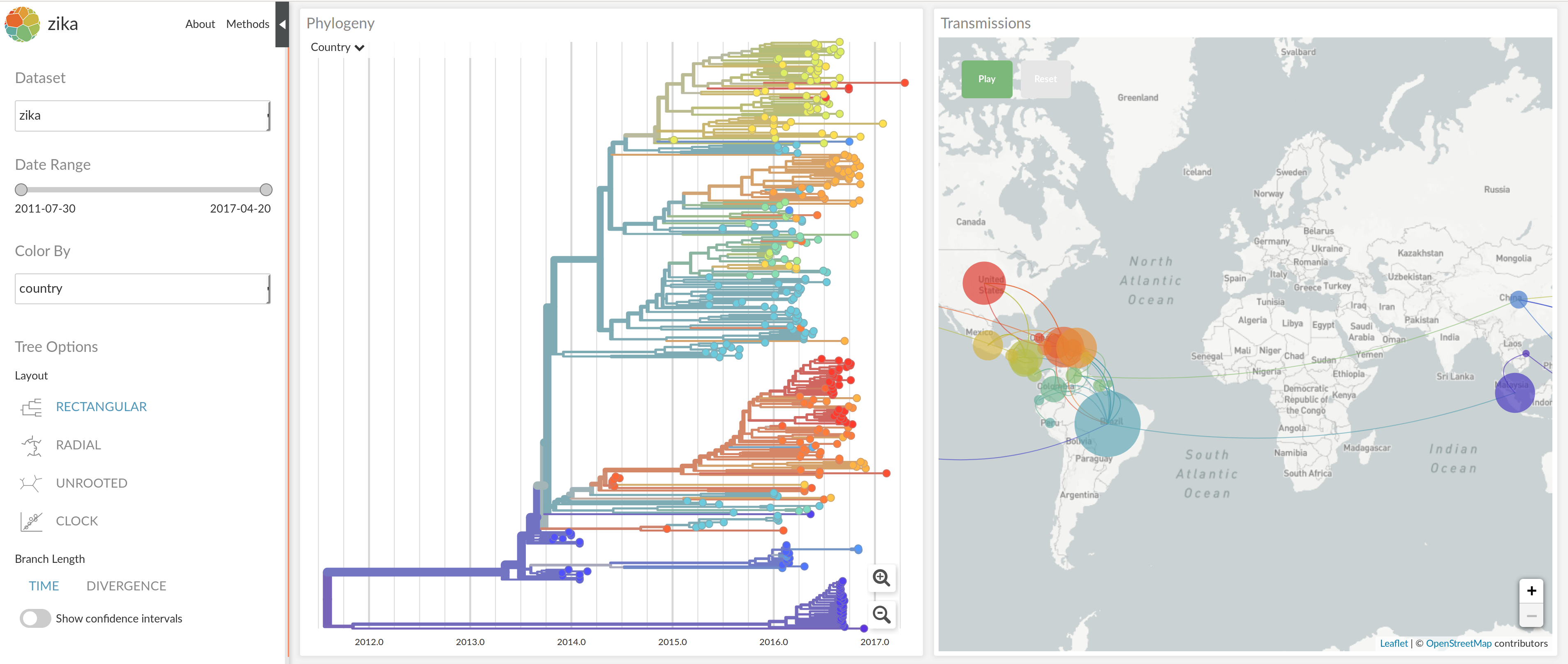
NextStrain architecture
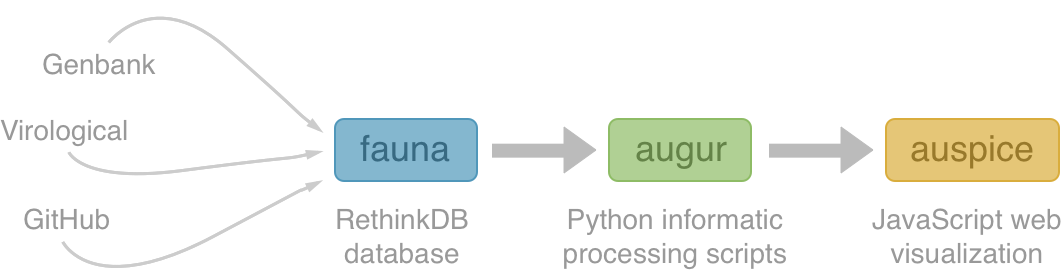
Using treetime to rapidly compute timetrees
TreeTime: maximum likelihood phylodynamic analysis
Phylogenetic trees record history:
- transmission
- divergence times
- population dynamics
- ancestral geographic distribution/migrations
Typical approach: Bayesian parameter estimation
- flexible
- probabilistic → confidence intervals etc
- but: computationally expensive
TreeTime by Pavel Sagulenko
- probabilistic treatment of divergence times
- dates trees with thousand sequences in a few minutes
- linear time complexity
- fixed tree topology
- github.com/neherlab/treetime
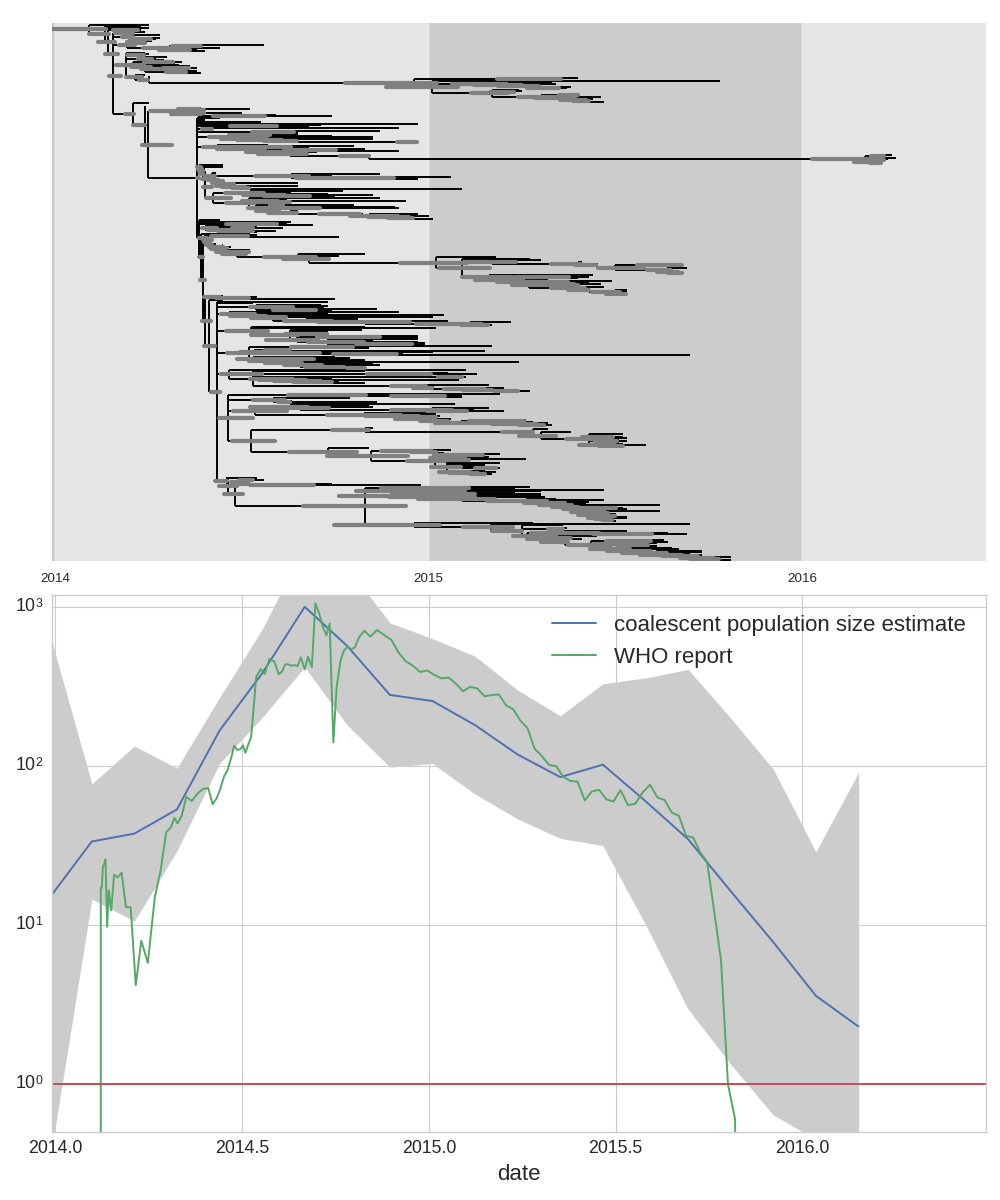
West African Ebola virus outbreak
TreeTime: nuts and bolts
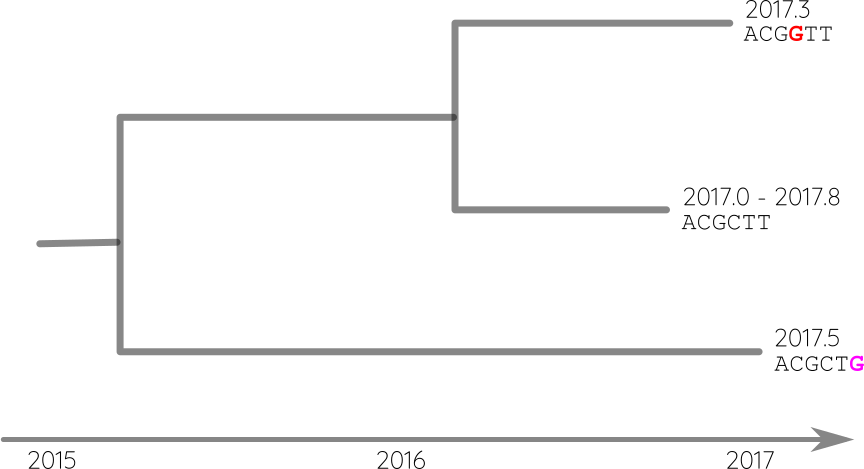

Attach sequences and dates
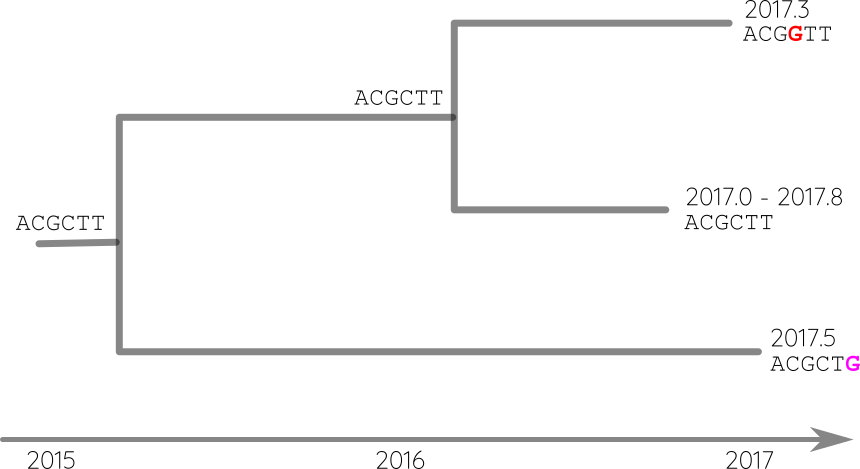

Reconstruct ancestral sequences
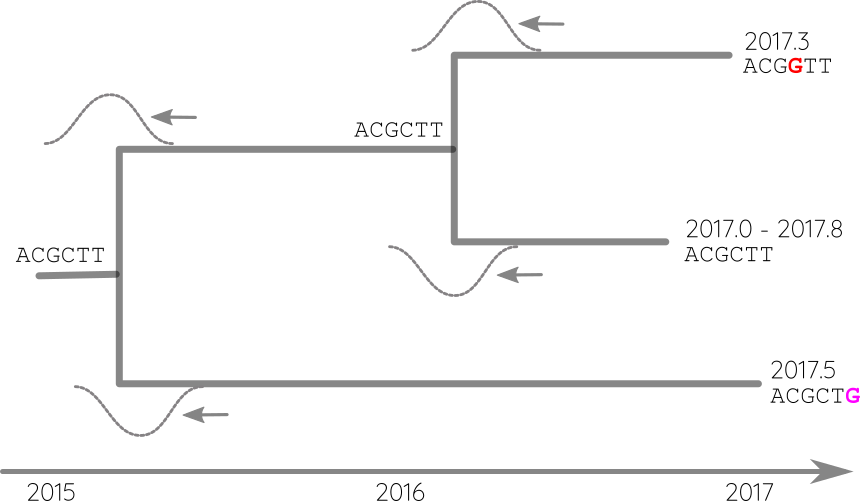
Propagate temporal constraints via convolutions
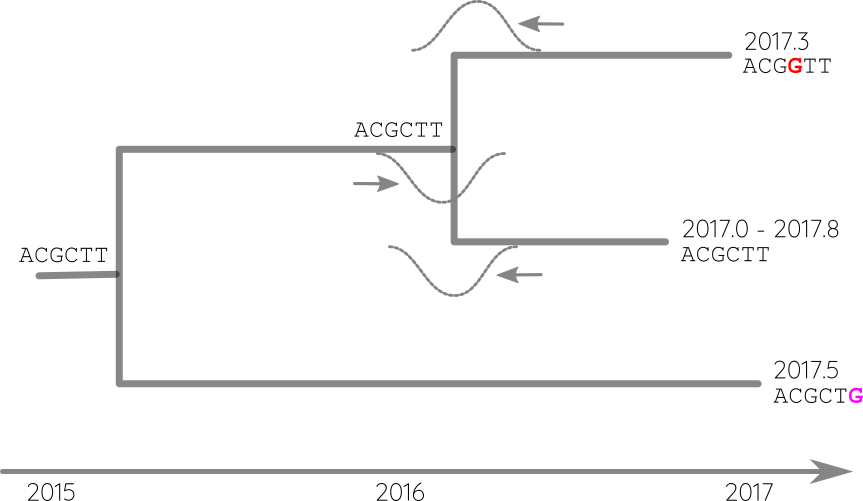
Integrate up-stream and down-stream constraints
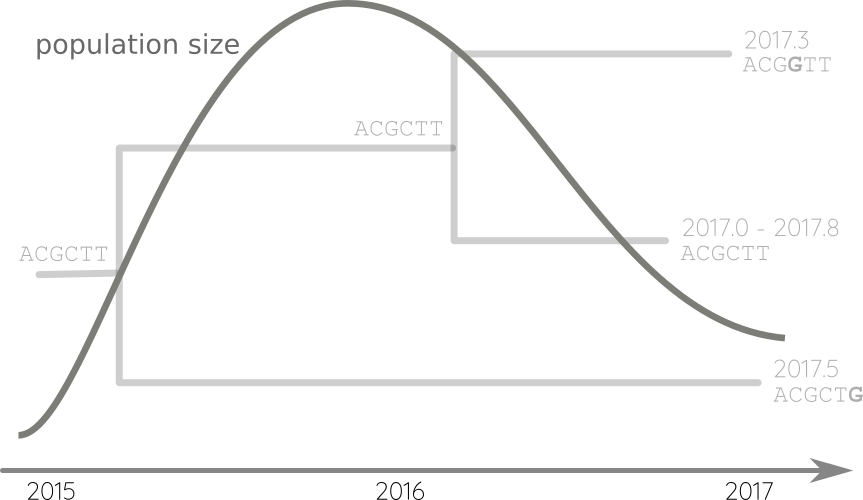
Fit phylodynamic model → iterate
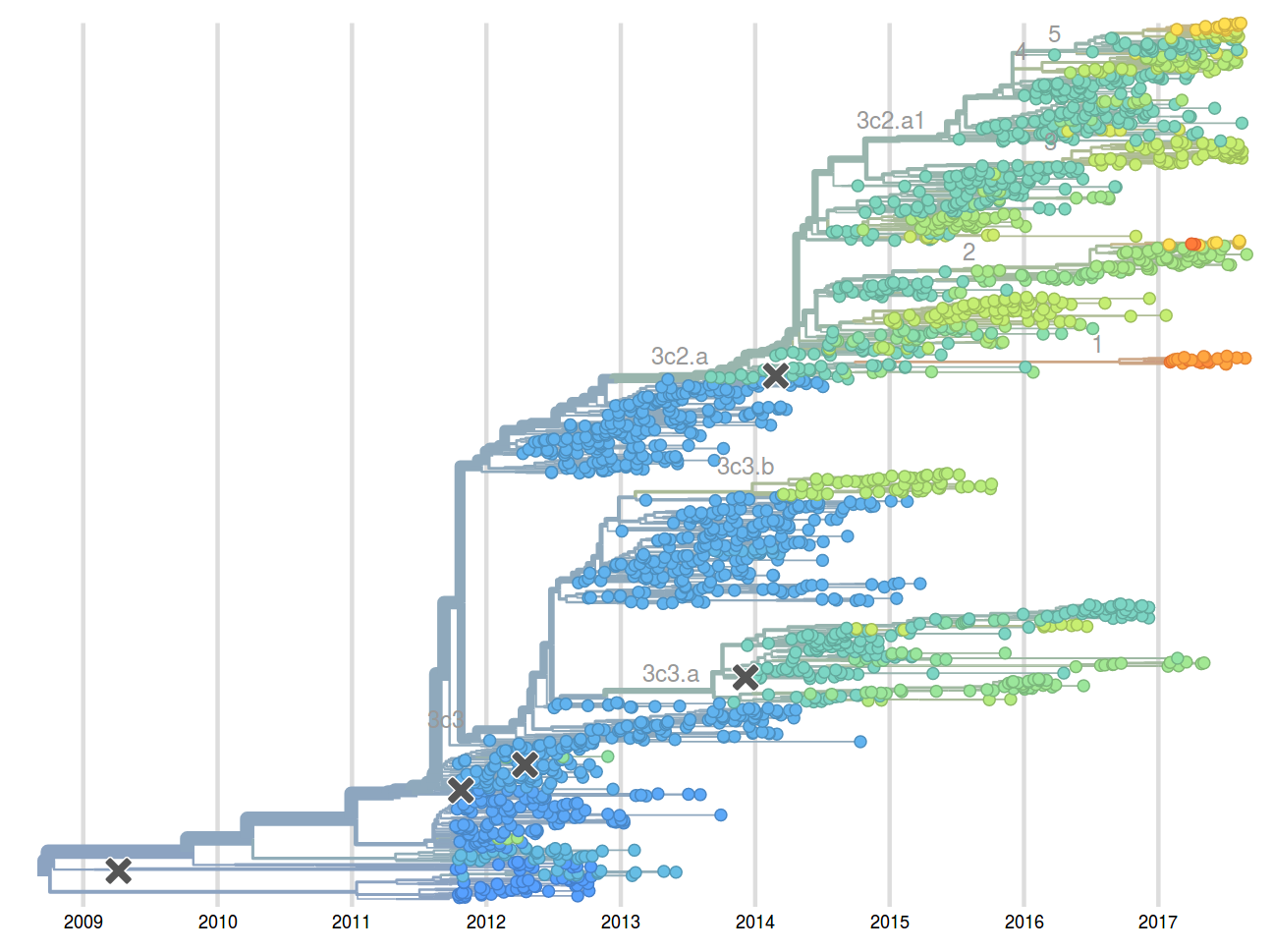
Molecular clock phylogenies of ~2000 A/H3N2 HA sequences -- a few minutes
What about bacteria?
- vertical and horizontal transmission
- genome rearrangements
- much larger genomes
- variation of divergence along the genome
- NGS genomes tend to be fragmented
- annotations of variable quality

panX by Wei Ding
- pan-genome identification pipeline
- phylogenetic analysis of each orthologous cluster
- detect associations with phenotypes
- fast: analyze hundreds of genomes in a few hours
- github.com/neherlab/pan-genome-analysis
panX @ pangenome.de
S. pneumoniae data set by Croucher et al.
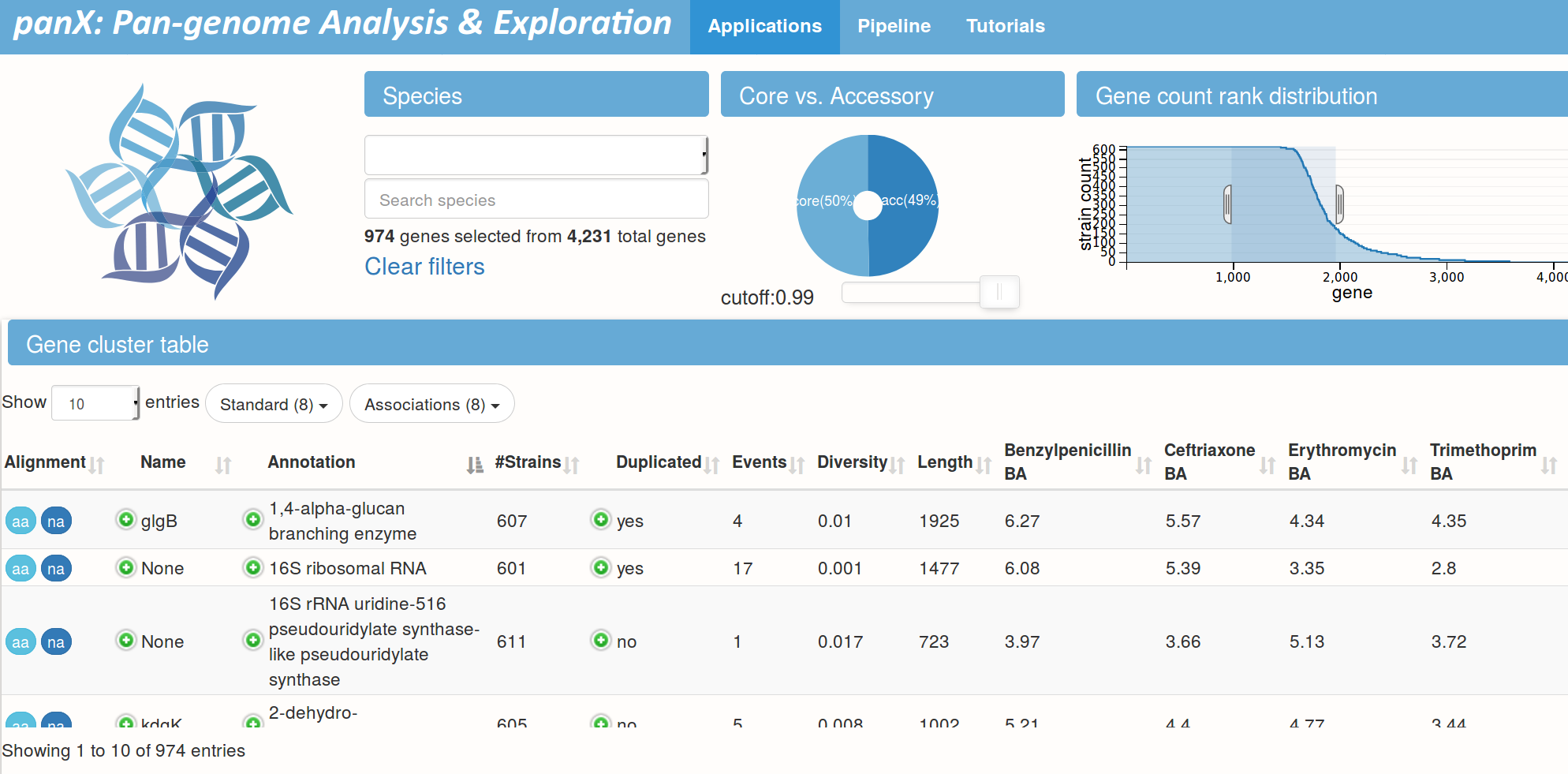
Pan-genome statistics and filters
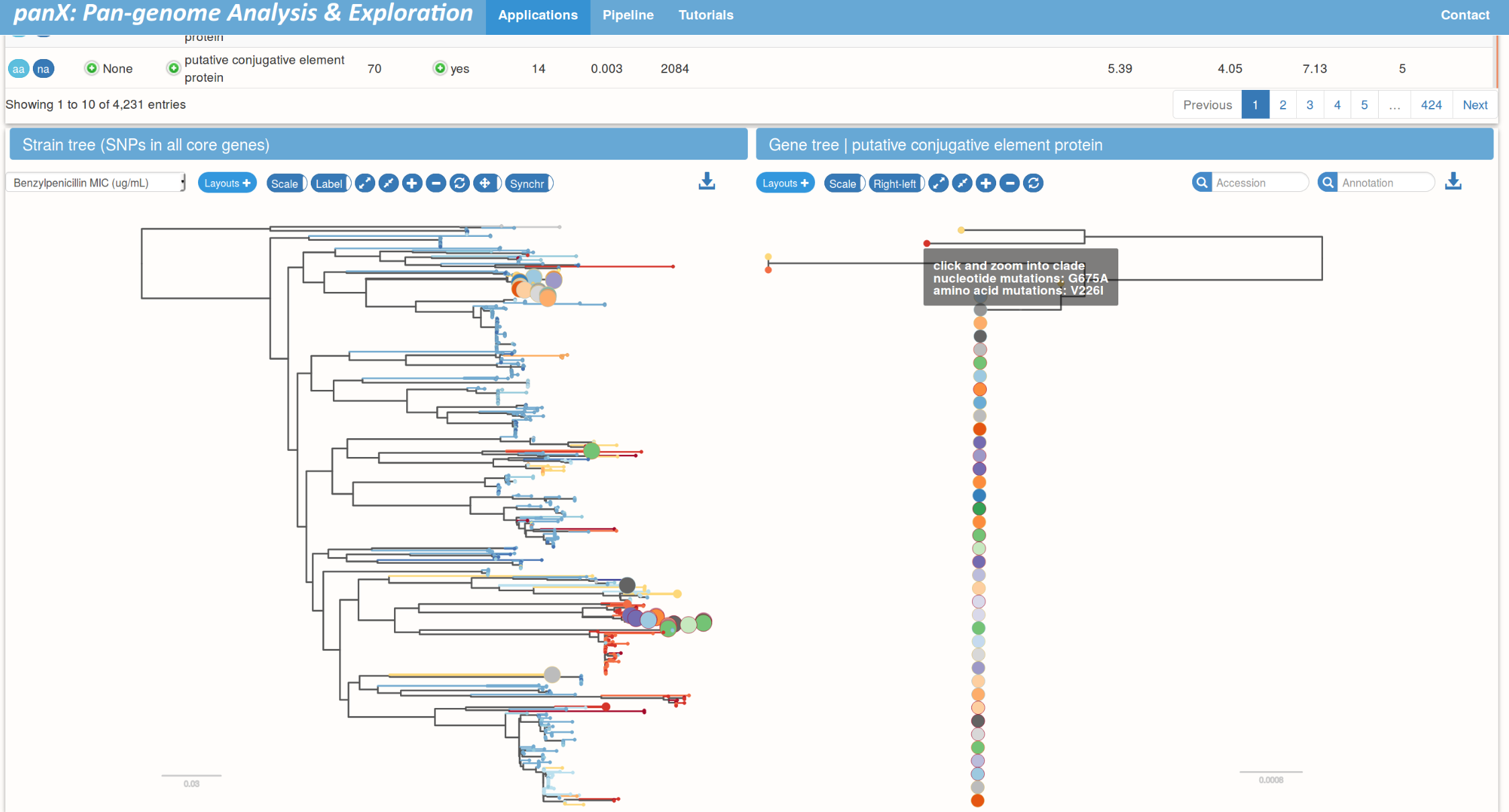
Species trees and gene trees
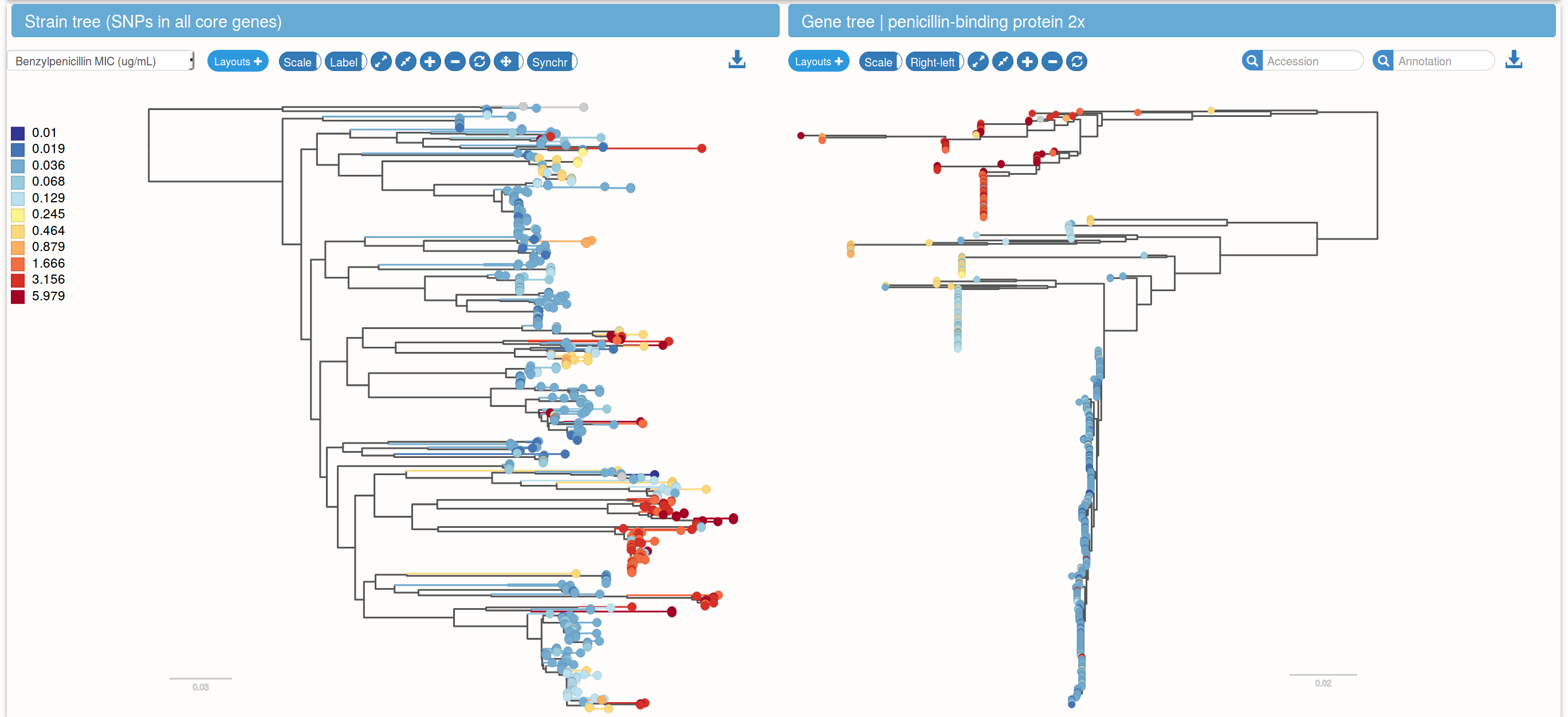
Links between species trees and gene trees
Summary
- Data set are growing rapidly
→ tools for interpretation and exploration are crucial - Breadth and depth
→ provide an overview, integrate, and go deep - Actionable outputs require (near)real-time analysis
→ fast analysis pipelines are essential - We are just scratching the surface...
Interested in HIV NGS: come find me!
Influenza and Theory acknowledgments




- Boris Shraiman
- Colin Russell
- Trevor Bedford
- Oskar Hallatschek
- All the NICs and WHO CCs that provide influenza sequence data



nextstrain.org




- Trevor Bedford
- Colin Megill
- Sidney Bell
- James Hadfield
- All the scientist that share virus sequence data




TreeTime & panX

TreeTime: Pavel Sagulenko
github.com/neherlab/treetimewebserver at treetime.ch
manuscript on bioRxiv

panX: Wei Ding
github.com/neherlab/pan-genome-analysislive site at pangenome.de
manuscript on bioRxiv



