In-vitro evolution of colistin resistance
Richard Neher
Biozentrum, University of Basel
slides at neherlab.org/201710_BZ.html
How we got into this...



Bianca Regenbogen
Colistin
- polymyxin, active against gram negatives
- interacts with outer membrane
- old antibiotic, discontinued because of nephrotoxicity
- today: last-resort antibiotic
mcr-1: "mobilized colistin resistance"
- first found in China 2 years ago
- now found in >30 countries
- mainly E. coli, Klebsellia, and Enterobacter
How does colistin resistance emerge in situ?
- How fast?
- Which mutations?
- Which order?
- Genetic background?
- Two P. aeruginosa strains from blood stream infections
- Extensively drug resistant phenotypes
- PA77:
- Plasmid 40kb, chromosome 3.7Mb, 2.3Mb, 1Mb contigs
- blaIMP-8, blaOXA-10, blaOXA-50
- various aminoglycoside resistance determinants
- fosfomycin resistance
- mostly on plasmid
- PA83:
- Plasmid 400kb, chromosome 6.8Mb
- blaVIM-2, blaOXA-50
- various aminoglycoside resistance determinants
- fosfomycin resistance
- in several integrons in the chromsome
From human patients to in-vitro experiments
Morbidostat by Toprak et al.
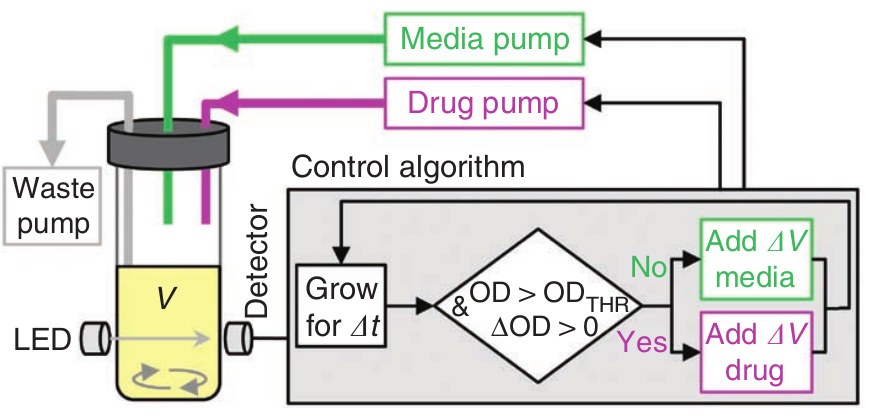
- Computer measures OD
- Controls pumps to add medium or AB
- Waste is removed
- Morbidostat→ growth rate is kept constant
- Chemostat → dilution is constant
- Turbidostat → OD is constant
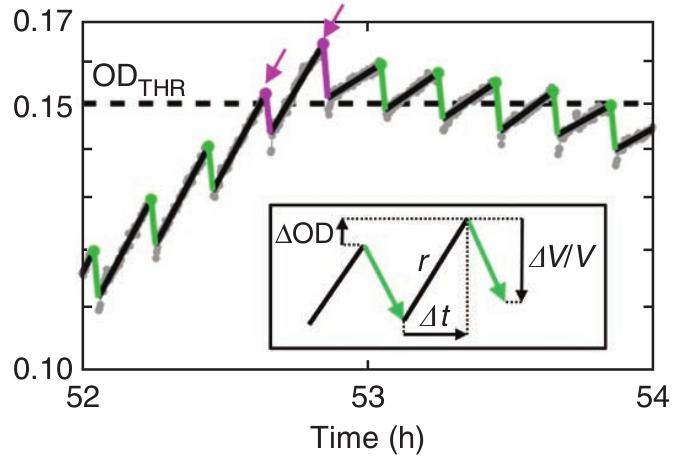
Our morbidostat
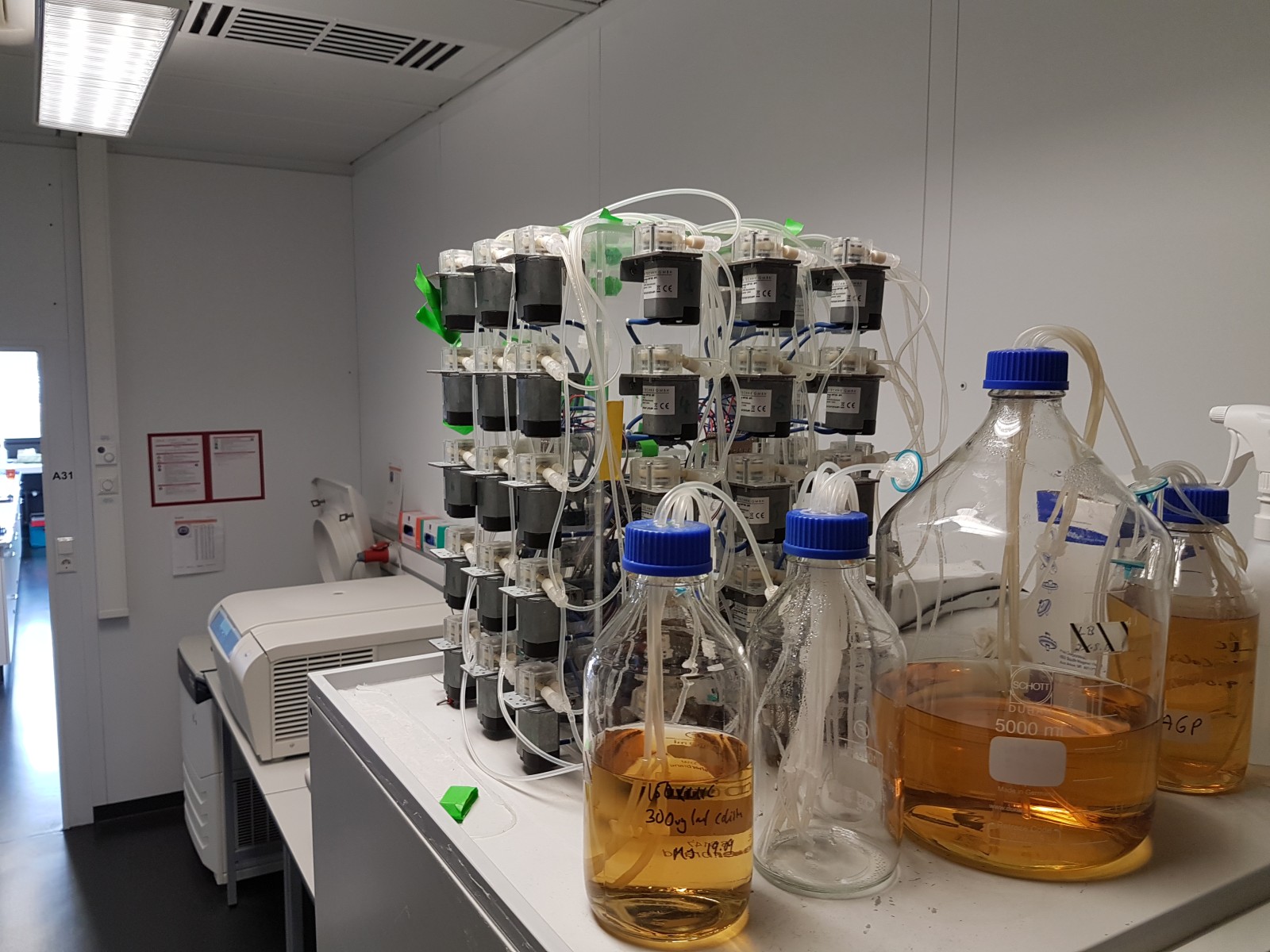

- more flexible software
- more compact design
- cheaper pumps and controllers
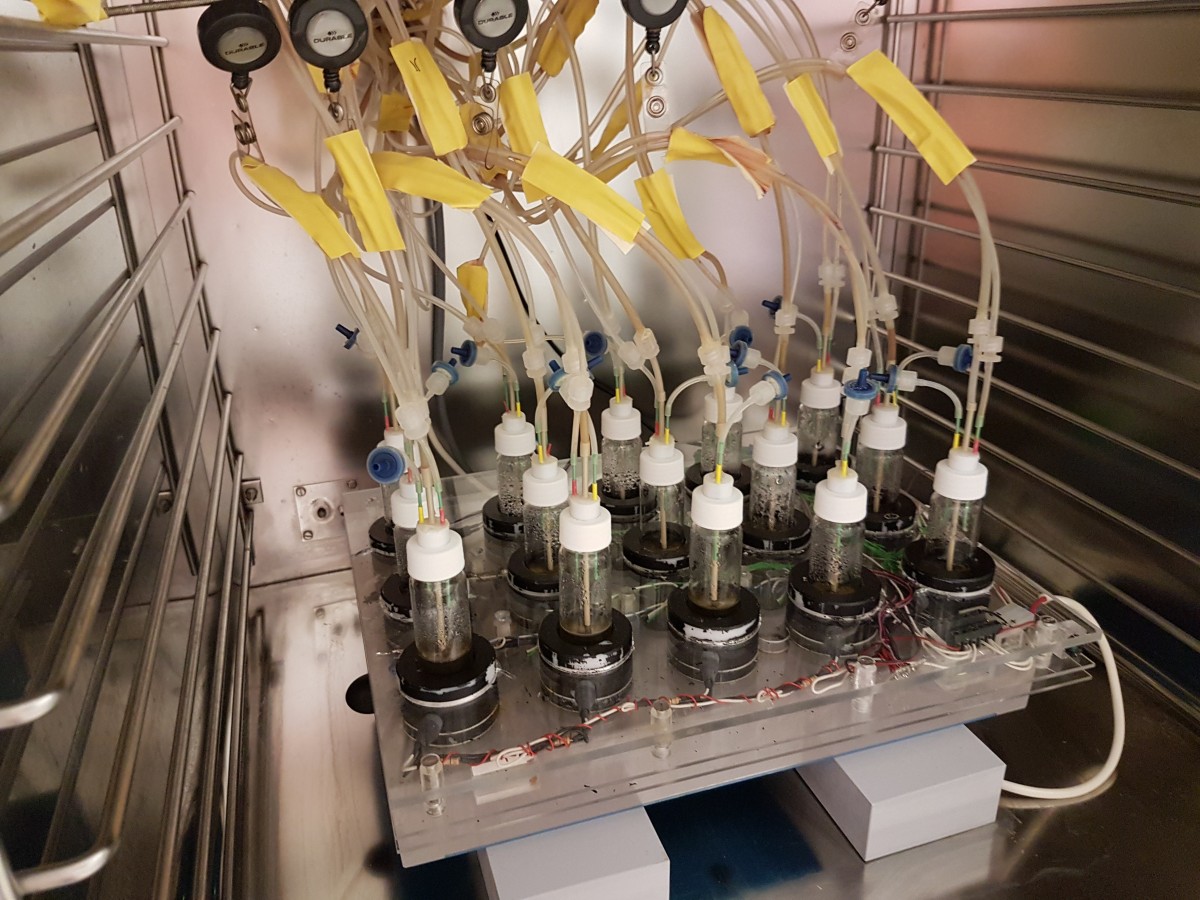


Running the morbidostat
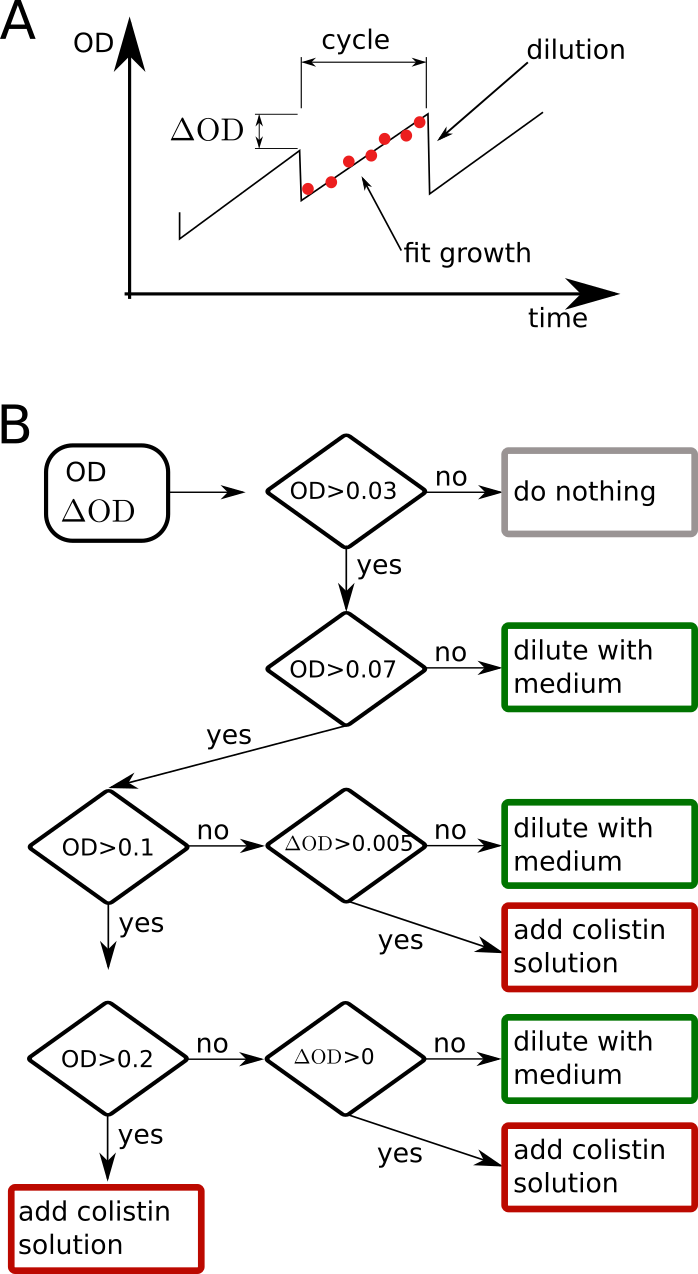
- Typically 10 cultures in parallel
- Measure OD every 30s
- Adjust AB conc every 10min
- Samples for sequencing every 2-3 days
- Total duration: 3weeks
- ~50'000 OD measurements per culture
- Most parts can be autoclaved
- Pumps sterilized with bleach/ethanol washes
- Replace vials every few days to avoid biofilms
- New piezo-pumps can be autoclaved as well
Colistin resistance emerges within 2 weeks
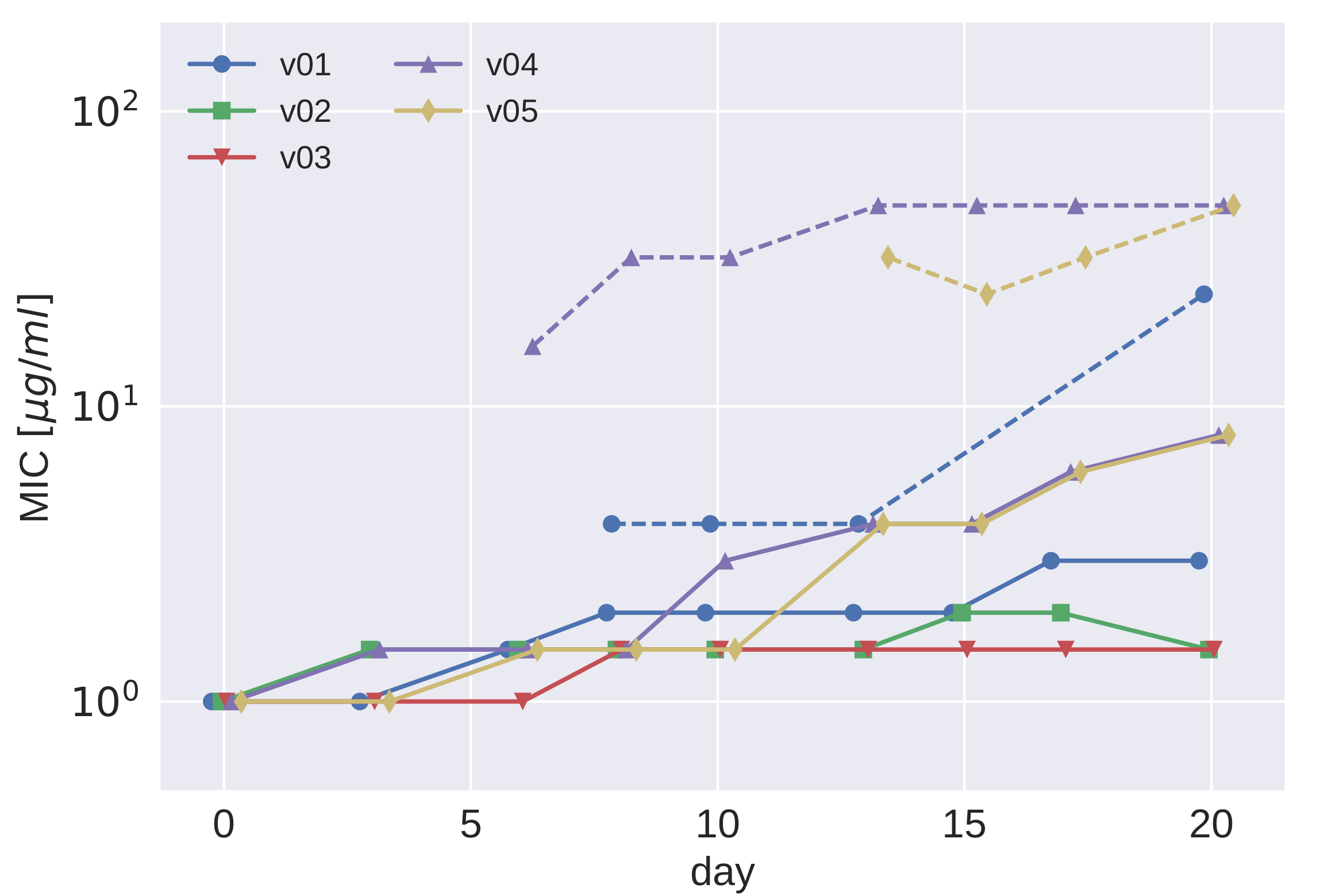
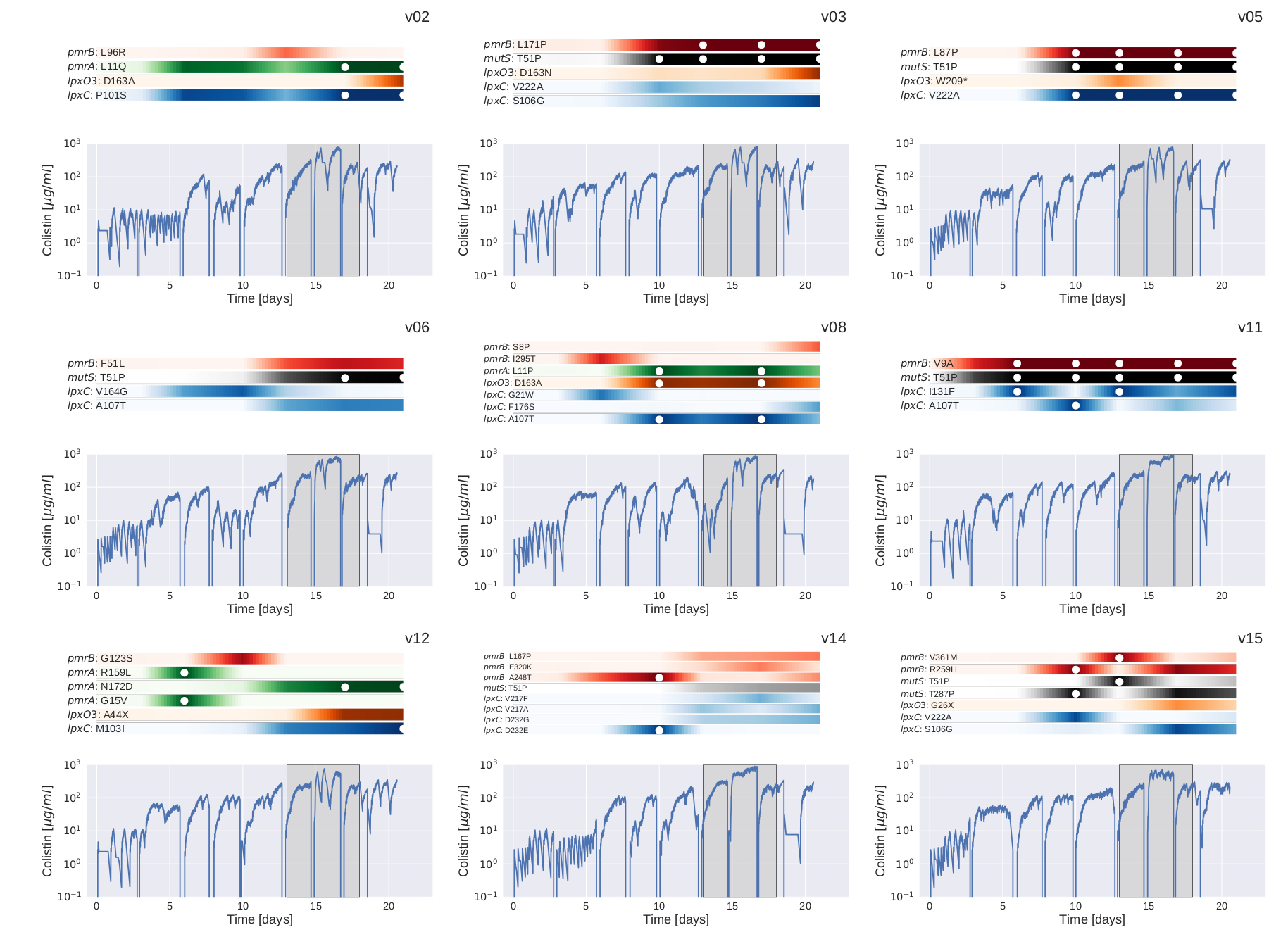
Mutation trajectories in strain PA77
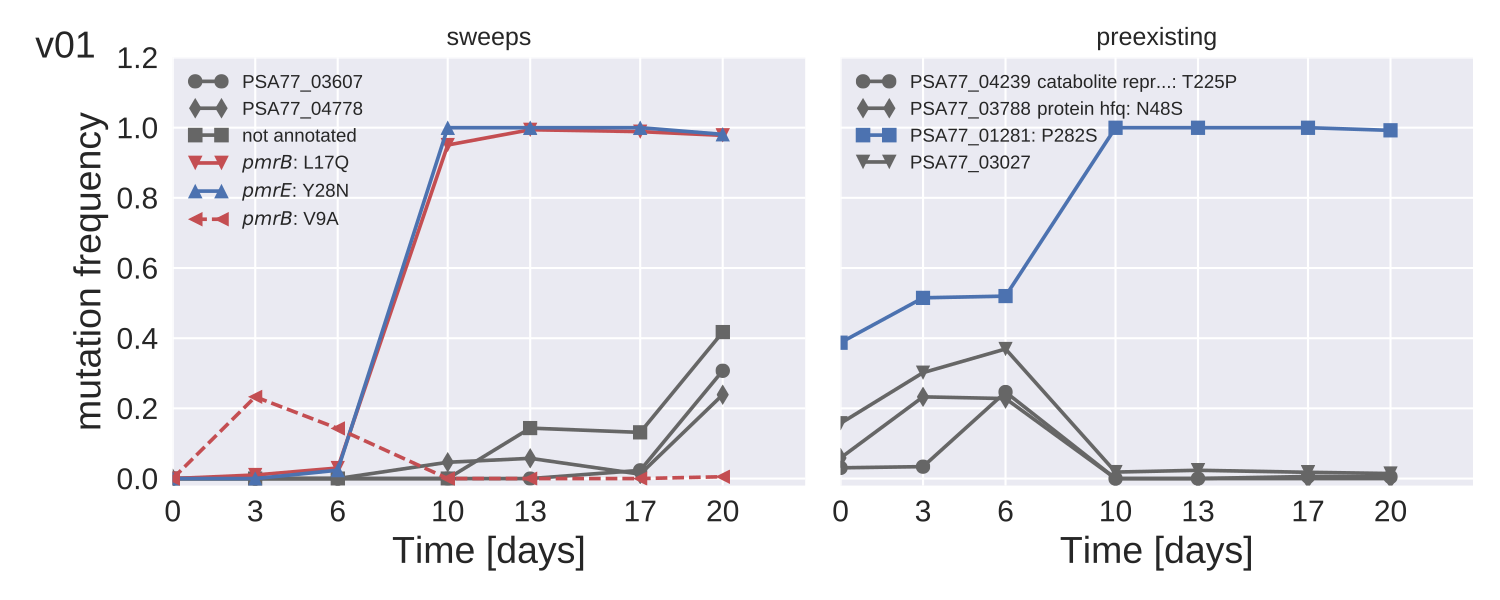
- Whole genome deep sequencing ($>200x$) with Illumina.
- Track rare mutations, no matter where they are
- Mutation frequencies to about 5% accuracy
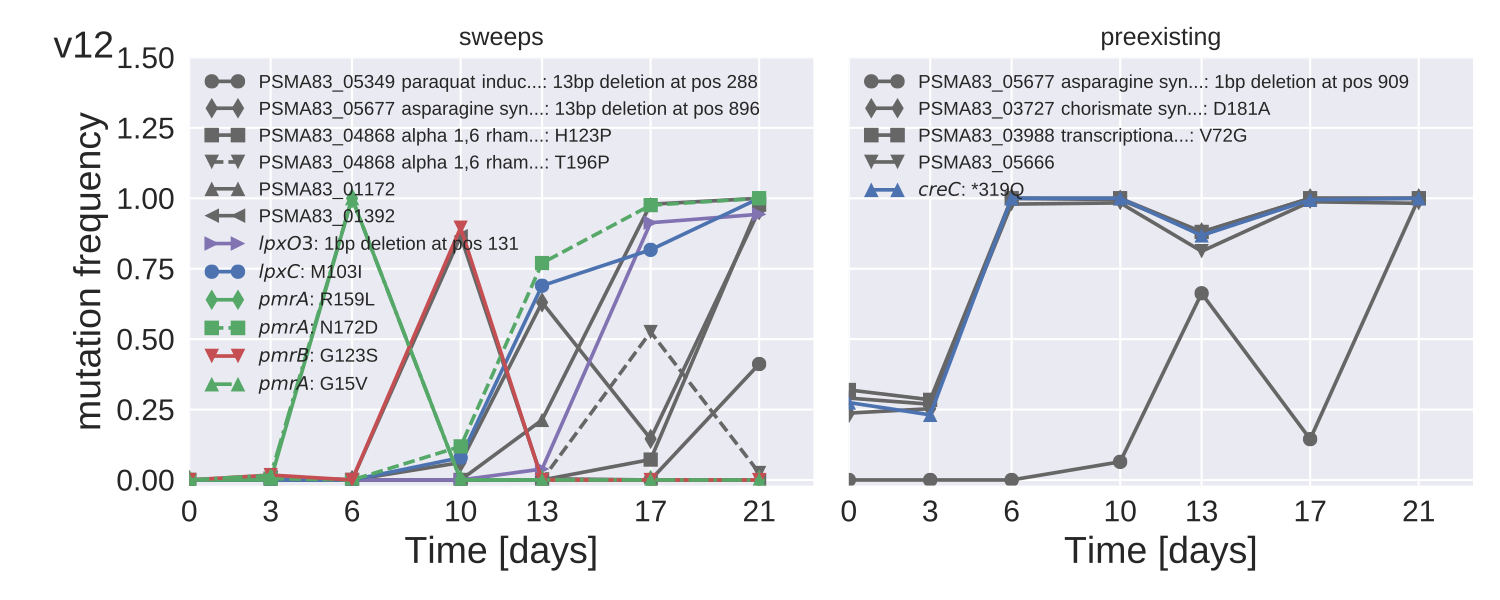
Mutation trajectories in strain PA83
Recurrent mutations PA77
| Gene | locus tag PAO1 | v01 | v02 | v03 | v04 | v05 | v05a | v08a | v10a | v11a |
| pmrB | PA4777 | V9A,L17Q | L90Q,E320K | V9A | P216Q | P254L | P169X,M292I | S257N | N41I,P169X | H261Y |
| pmrE | PA2043 | Y28N | Y28C | Y28N | Y28C | Y28N | Y28C | Y28C | Y28N | Y28N |
| lptD | PA3559 | Y803X | L538R |
- pmrE: Most PA strains are 28C → reversion
- pmrB: Many mutations that constitutively activate the gene
→ canonical colistin resistance gene - lptD: code for outer membrane protein, LPS transport.
→ has been associated with colistin resistance in Acinetobacter
Recurrent mutations in PA83
| locus tag PAO1 | v02 | v03 | v05 | v06 | v08 | v11 | v12 | v14 | v15 | |
| lpxC | PA4406 | P101S | V222A,S106G | V222A | V164G,A107T | A107T,G21W,F176S | A107T,I131F | M103I | D232E,D232G,V217F,V217A | V222A,S106G |
| pmrB | PA4777 | L96R | L171P | L87P | F51L | S8P,E320K | V9A | G123S | E320K,A248T,L167P | R259H,V361M |
| putative tranferase | PA3853 | C226G | Y3C,G62S | V34A,Y155C | C226G | R60C,Y216C,E185G | C226G | V122A,E185G | ||
| asparagine synthetase | L365P | frameshift | L425P | G32S | frameshift | W153* | L365P,W153*,V286M | |||
| migA | PA0705 | H219P | C25R,N27S | D106G | Q191R,V22A | T196P,H123P | H219P | A168T | ||
| mutS | PA3620 | T51P | T51P | T51P | T51P | T51P | T51P,T287P | |||
| lpxO2 | PA0936 | D163A | D163N | W209* | D163A | frameshift | in-frame deletion | |||
| pmrA | PA4776 | L11Q | L11P | R159L,G15V,N172D | ||||||
| cupB5 | PA4082 | G260X,R26C | P139P | |||||||
| pdtA | PA0690 | A3885V,A3885A | G1527X | |||||||
| morA | PA4601 | R1199H | G143D | |||||||
| lpxA | PA3644 | R96S | R191C | |||||||
| priA | PA5050 | L38L | R689R | |||||||
| traN | W773* | G912D | ||||||||
| wbpM | PA3141 | E273K | E273G | |||||||
| mscL | PA4614 | V86I | S35P |
- lpxC: lipid A biosynthesis
- pmrB: Many mutations that constitutively activate the gene
→ canonical colistin resistance gene - lptD: code for outer membrane protein, LPS transport.
→ has been associated with colistin resistance in Acinetobacter
Mutations in pmrAB
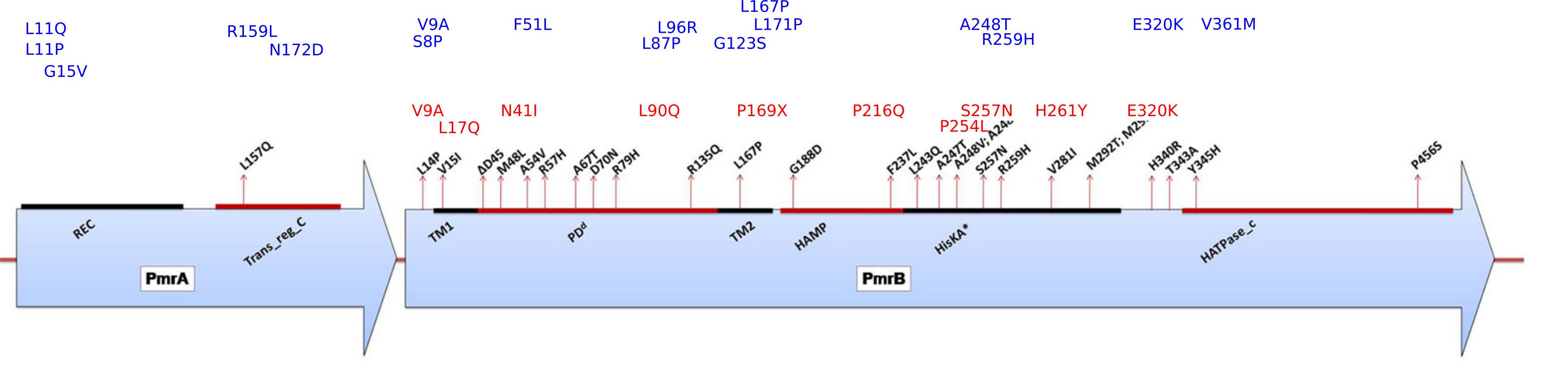 Previously observed and new mutations in pmrAB (blue: PA83, red: PA77)
Olaitan et al. Front. Micro., 2014
Previously observed and new mutations in pmrAB (blue: PA83, red: PA77)
Olaitan et al. Front. Micro., 2014
Mutator strains
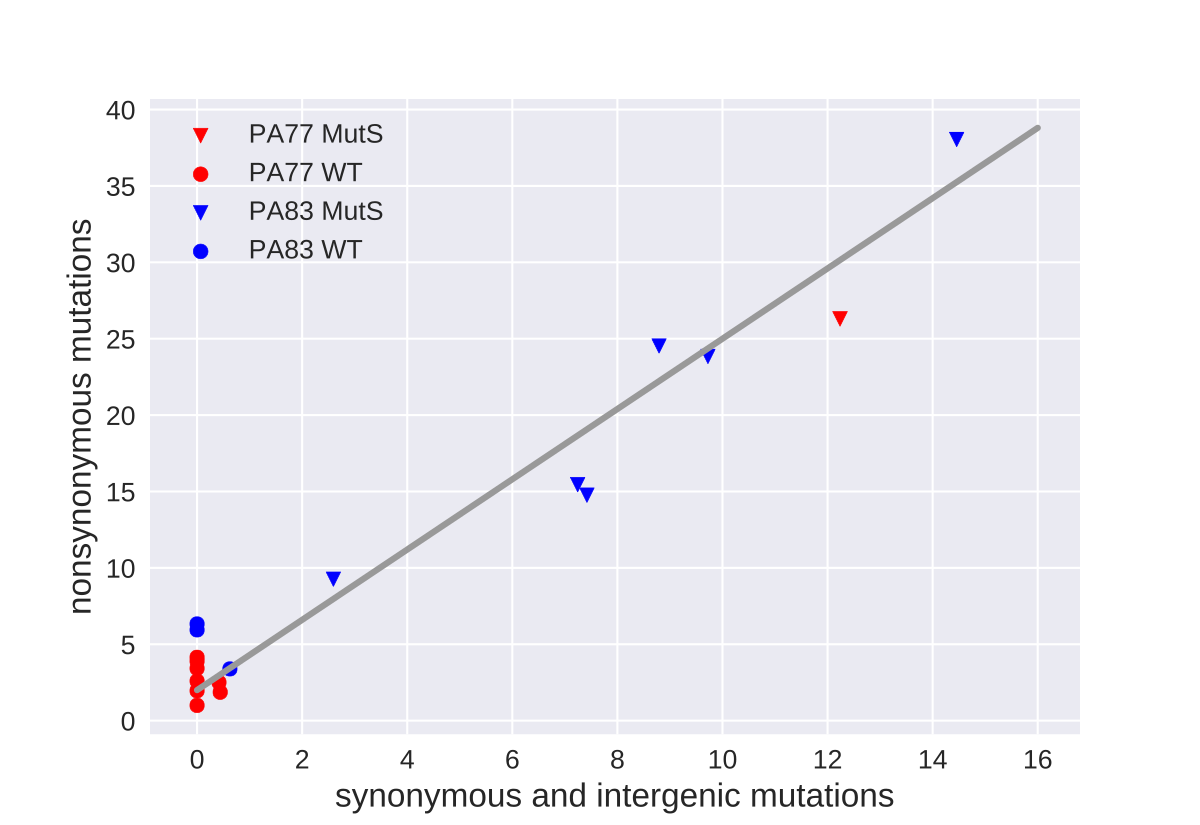
- 1/9 PA77 cultures developed mutator phenotypes
- 6/9 PA83 cultures developed mutator phenotypes
- about 10-100 fold more mutations, mostly unique
- non-mutator: almost only non-synonymous mutations
- mutator: pretty random mix
- mutator/non-Mutator develop resistance at similar speed/similar mutations
Insertions and deletions
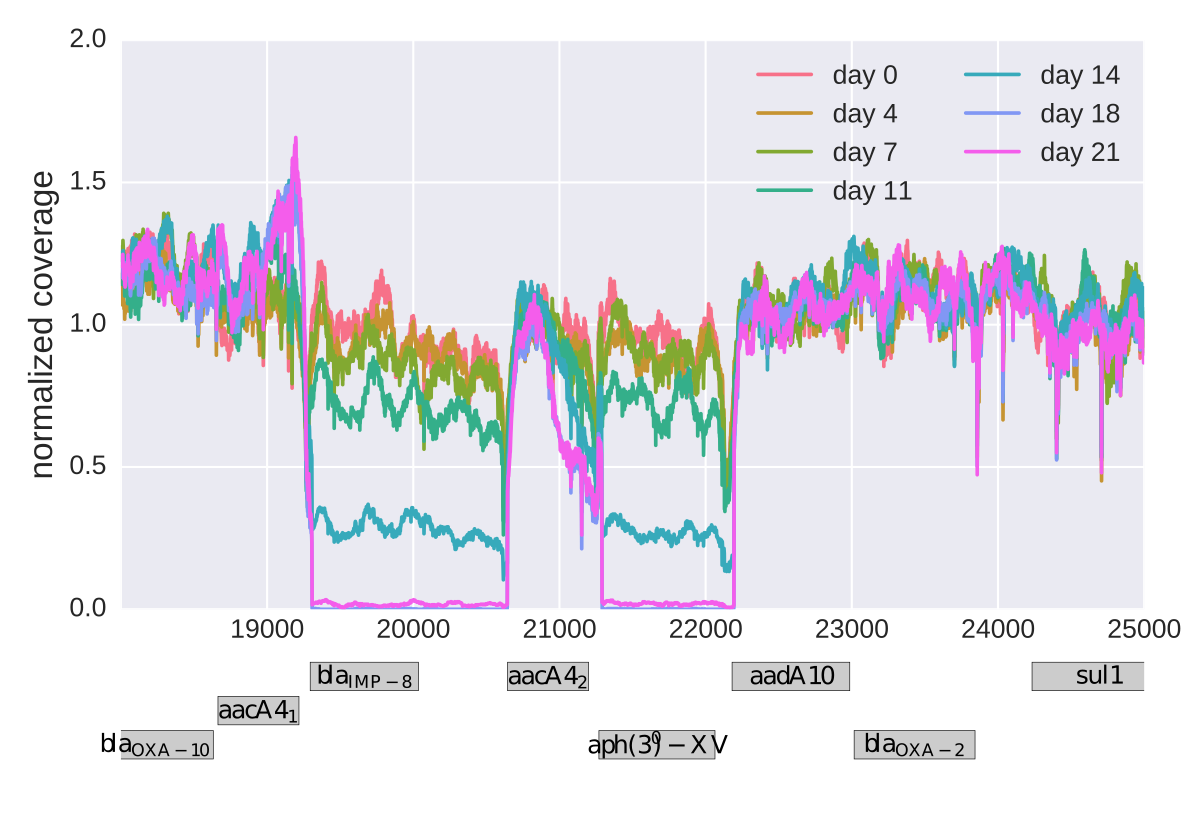
Stable genome!
- few large deletions
- a small number if gene-inactivating deletions
- one notable progressive loss of parts of the resistance plasmid in one PA77 strain
Comparison of the two strains
PA77
- few mutations
- pmrB: universal, different positions
- pmrE: reversion at specific position
- one mutator
- resistance increased around at day 8-10
PA83
- messy -- many mutations
- lpxC, pmrB: universal, different positions
- migA, pmrA, lpxO2: common, different positions
- 6 out of 9 mutators, possibly prexisting
- resistance increased around at day 5-6
Take home:
- pmrB is a common core of colistin resistance
→ 2-component system that regulates LPS modification - otherwise strain specific mutation trajectories, mostly involving LPS mods
- Very reproducible in the same strain
- Phenotypic trajectories are similar
- No strict order, but pmrB tends to mutate first
High quality reference genomes and high coverage are essential
- without good reference, lots of artifactual polymorphisms
- duplicated regions are collapsed in mapping/assembly → spurious diversity
- obtaining good references is straightforward with long read sequencing (PacBio/nanopore)
- Illumina coverage is a poor guide of duplications. Only relative differences in coverage are meaningful.
- mutations that change in frequency are most likely real than SNPs that remain at similar frequency (need high coverage)
Potential of morbidostat-like devices
Quantities that can be monitored:
- features that can be captured by a camera or photodetector
- optical density
- fluoresence
- ...
Control:
- additions of several different solutions
- each vial can be individually addressed
- rapid feedback on measured parameters
- custom schedules (e.g.~pharmacokinetics)
- vary temperature, light, etc
Prerequisites/challenges
- electronic and mechanical workshop
- a bit of programming
- with flexibility comes the need to specify
- lots of media
- avoiding contamination
- ...
Acknowledgements
- Bianca Regenbogen, now Uni Hohenheim
- Silke Peter, UKT Tübingen
- Matthias Willmann, UKT Tübingen

