Tracking and predicting the spread of pathogens and resistance
Richard Neher
Biozentrum, University of Basel
slides at neherlab.org/201903_HMS.html
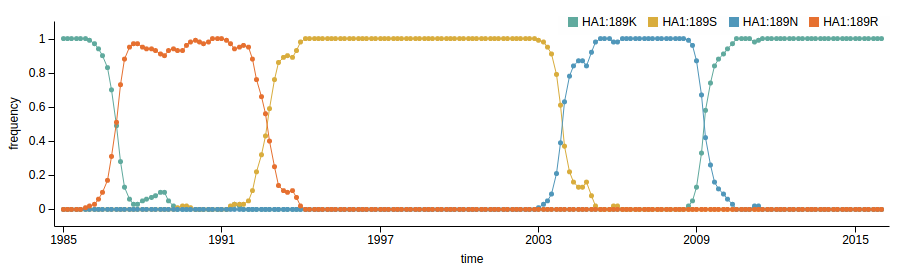
Human seasonal influenza viruses
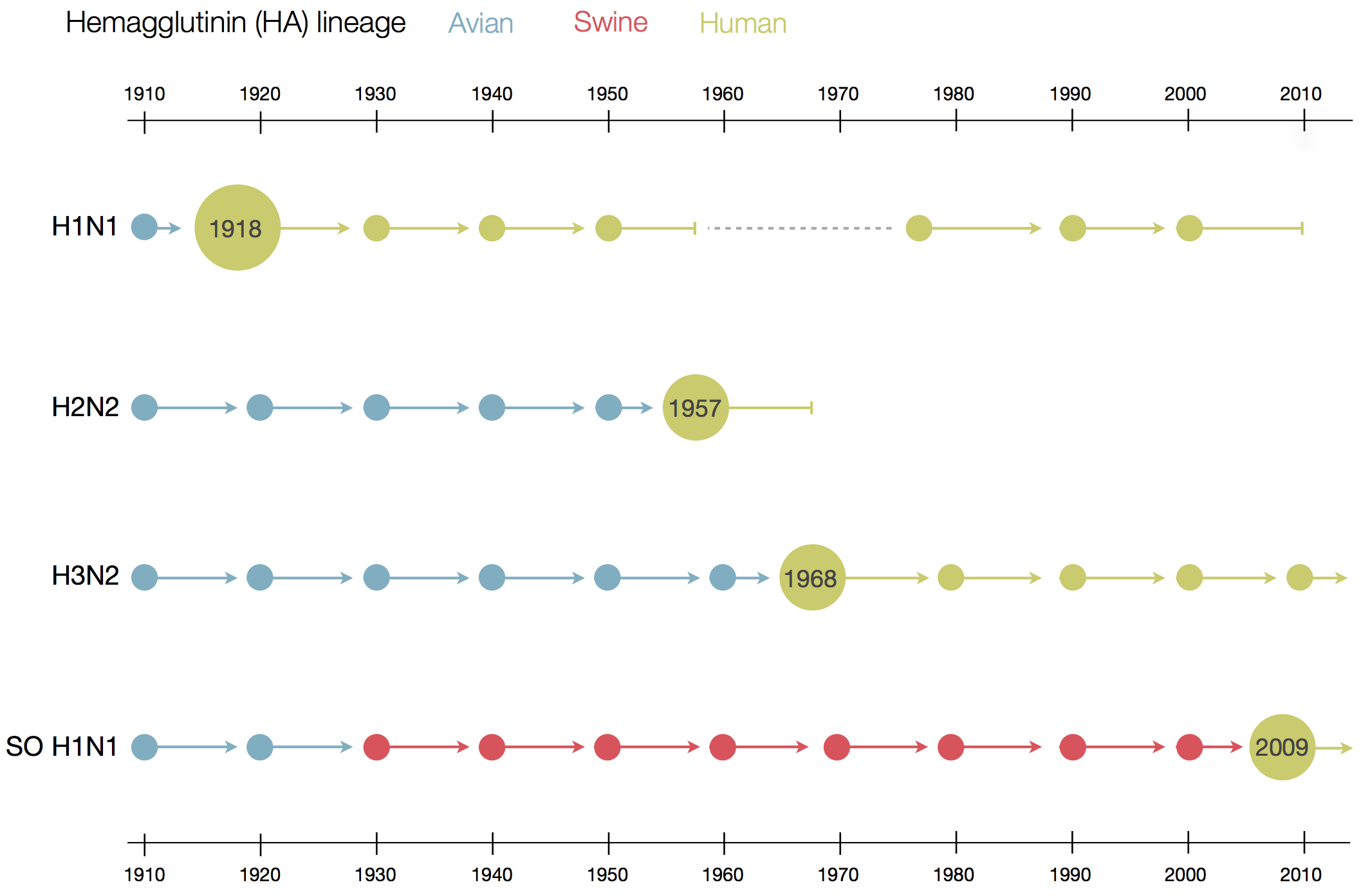
Sequences record the spread of pathogens
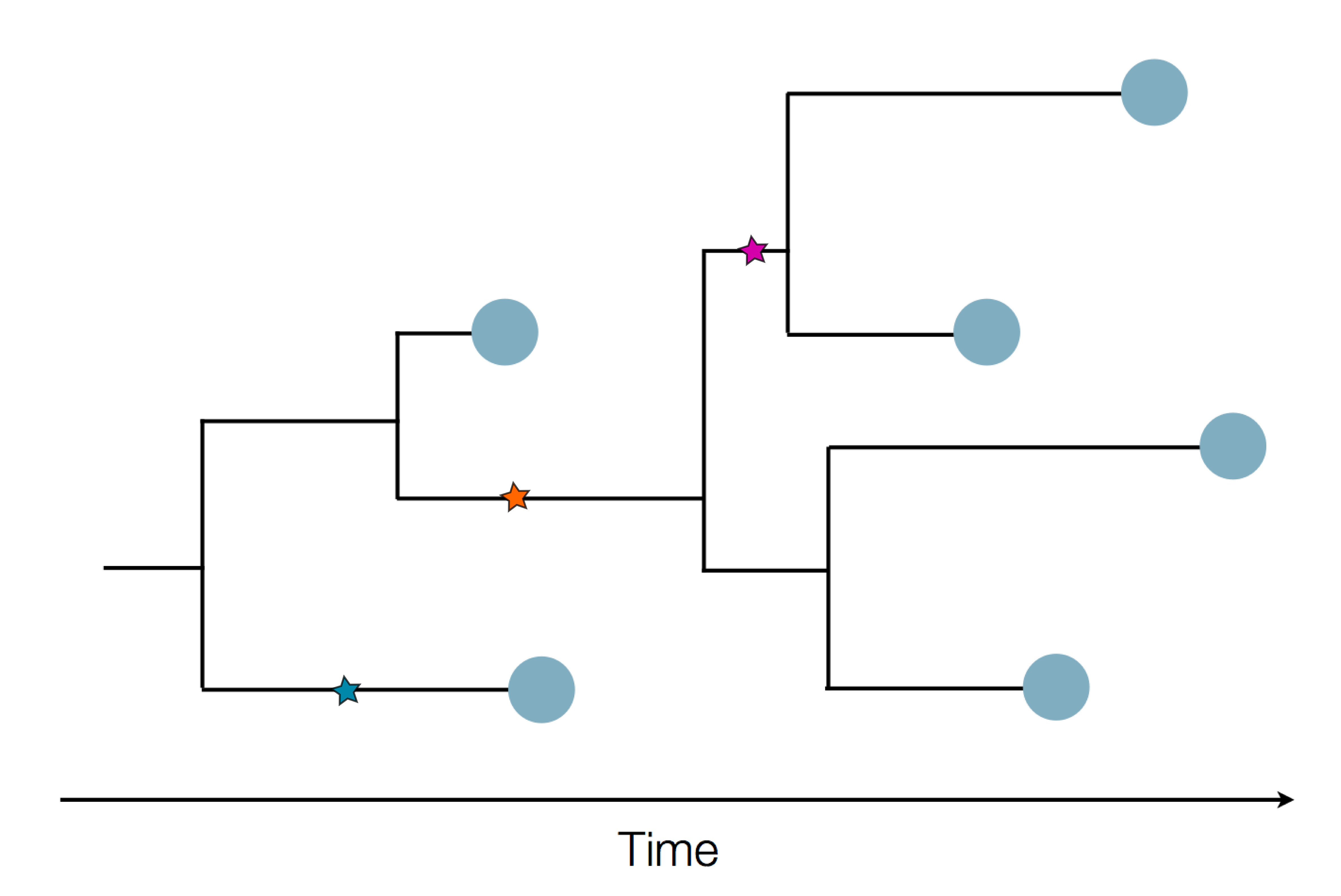
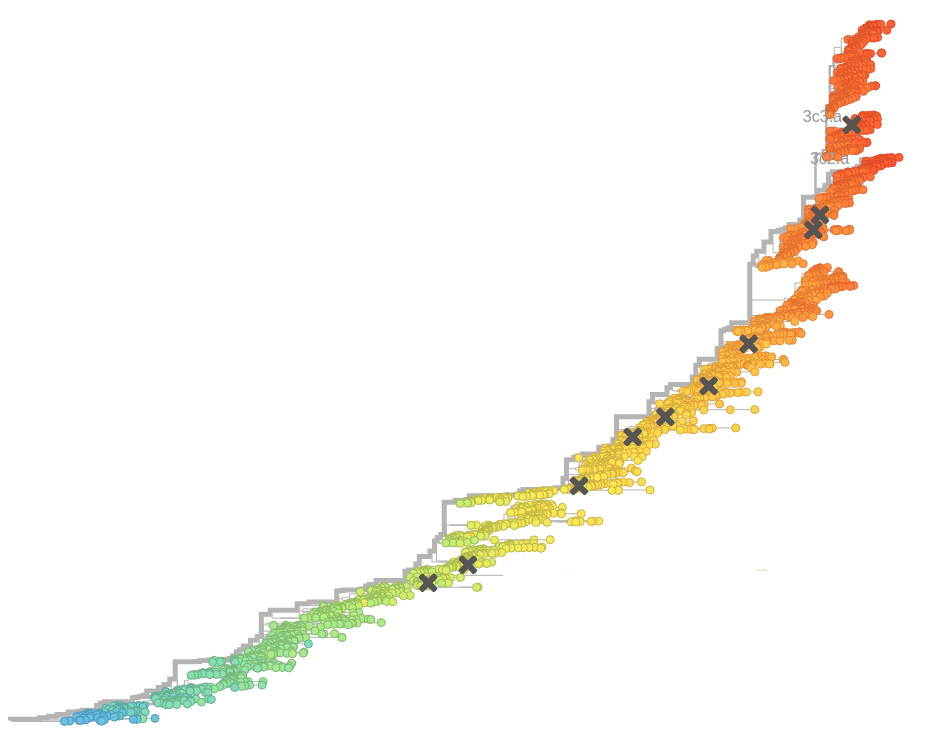
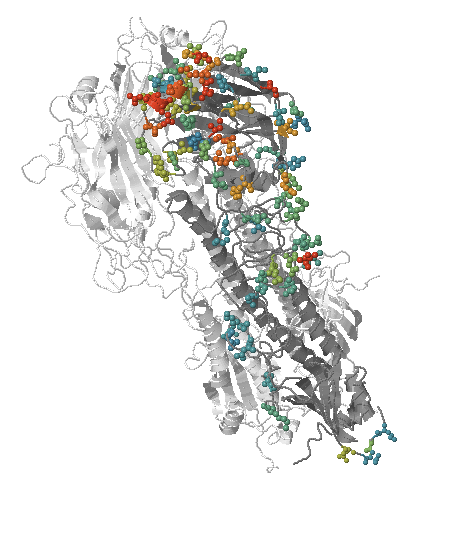
- Influenza viruses evolve to avoid human immunity
- Vaccines need frequent updates
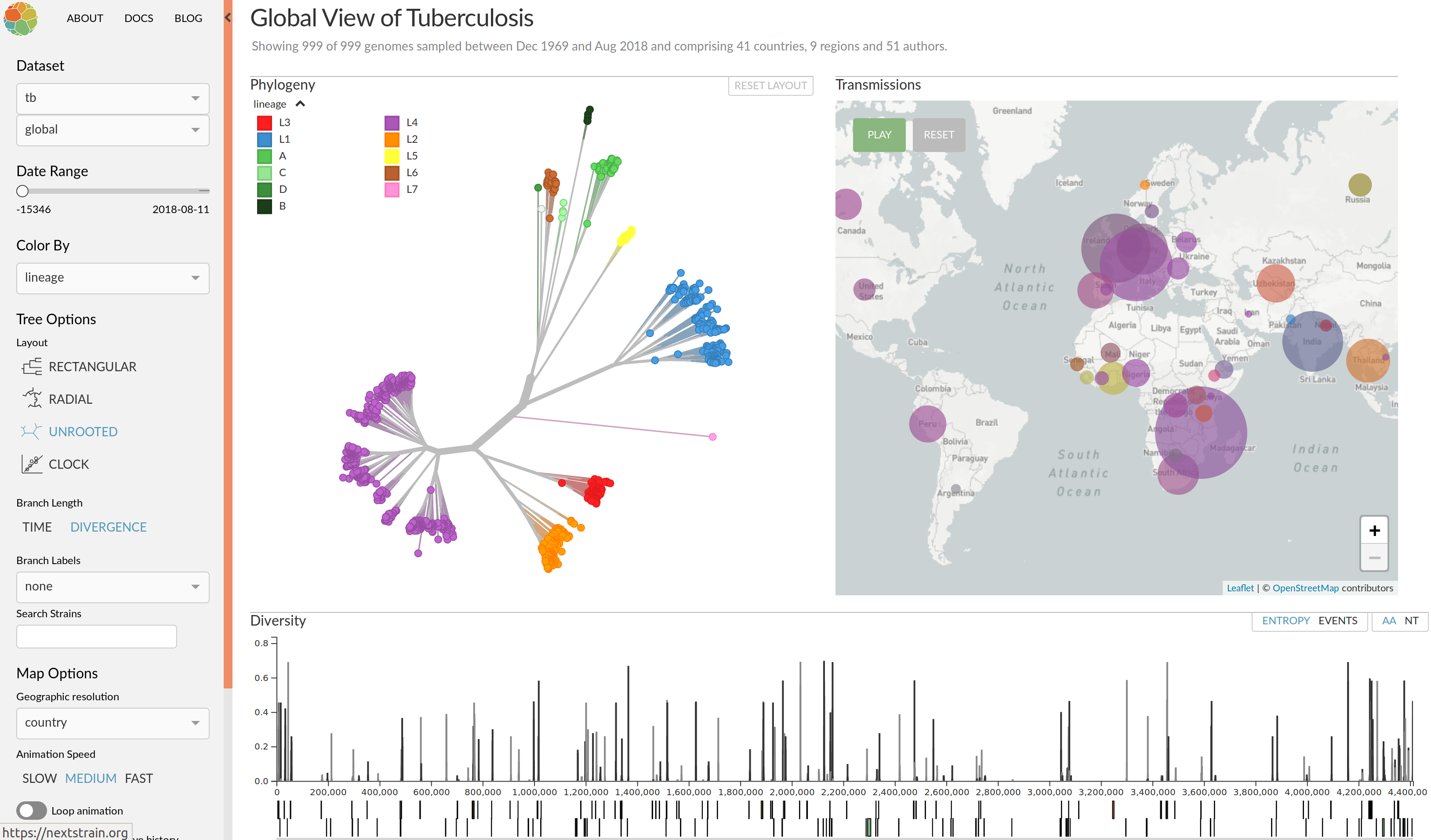
nextflu.org
joint work with Trevor Bedford & his lab
Beyond tracking: can we predict?
Fitness variation in rapidly adapting populations
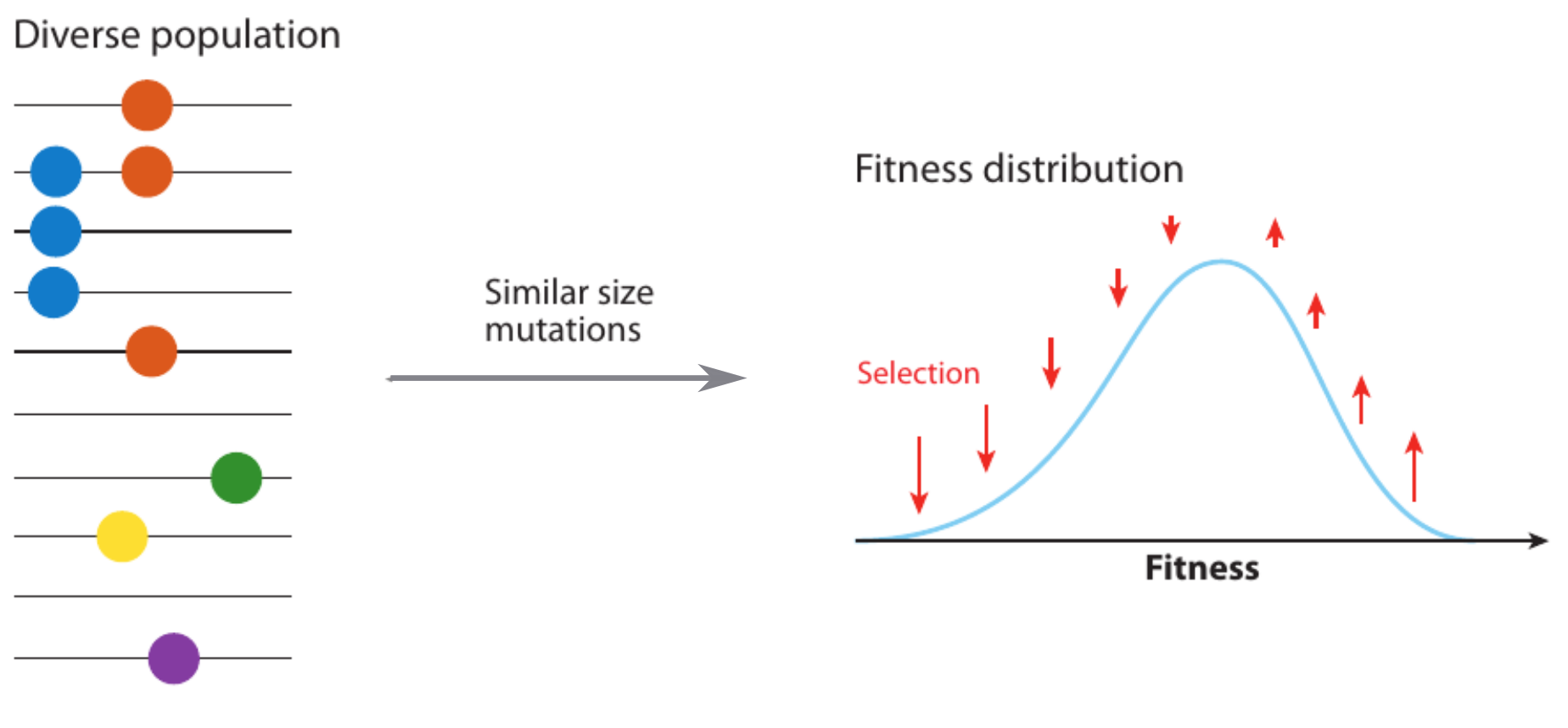
- Speed of adaptation is logarithmic in population size
- Environment (fitness landscape), not mutation supply, determines adaptation
- Different models have universal emerging properties
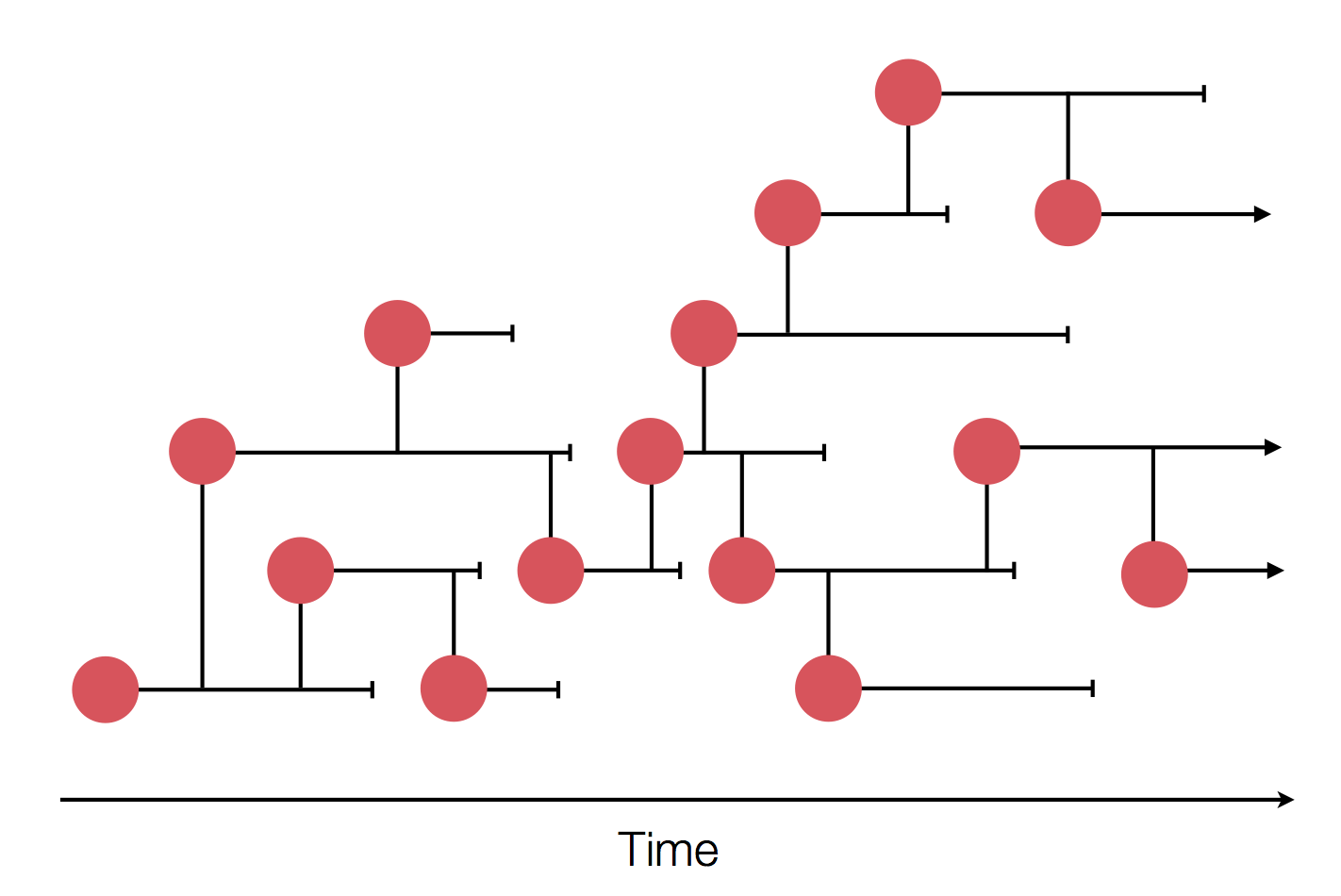
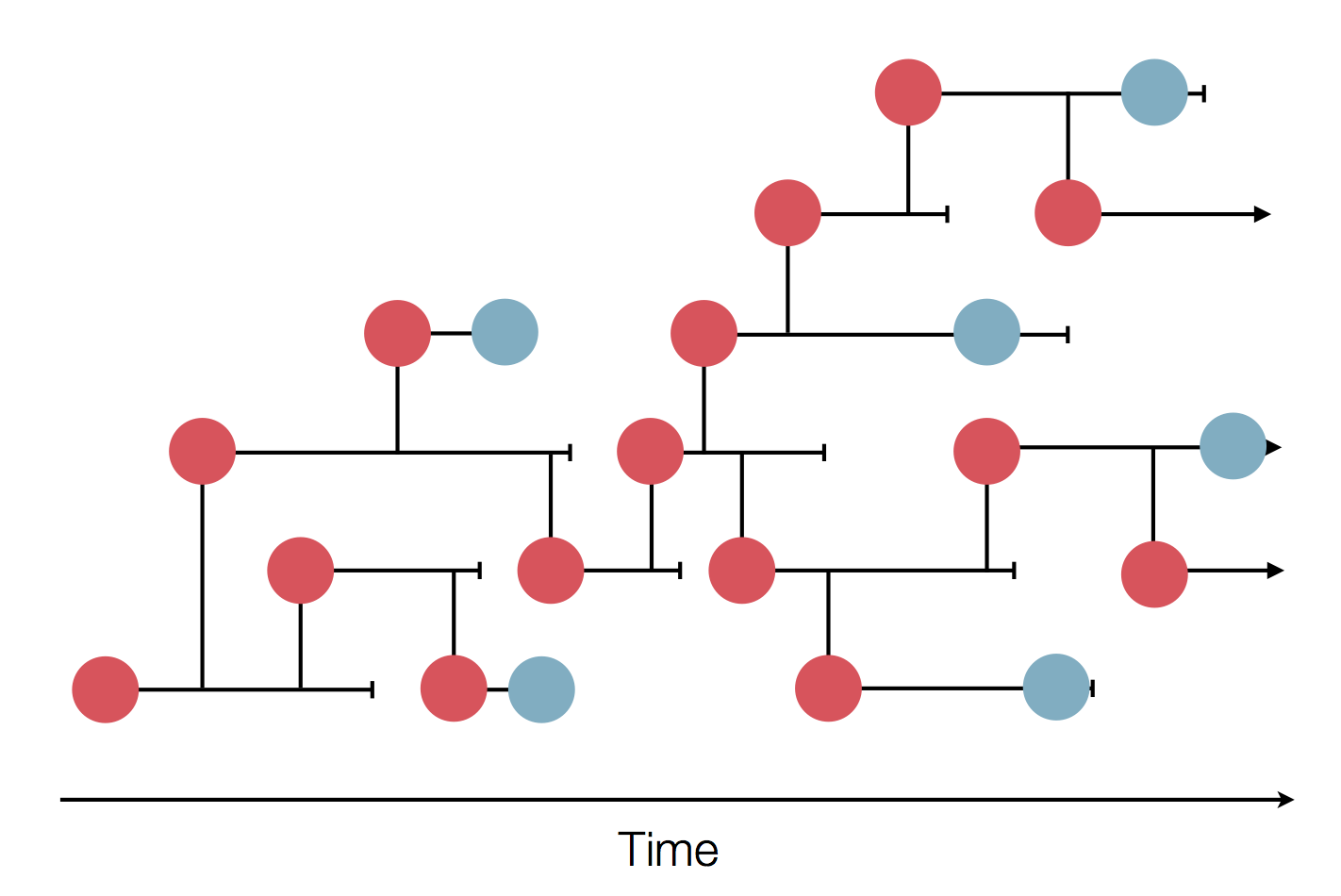
Neutral/Kingman coalescent
strong selection
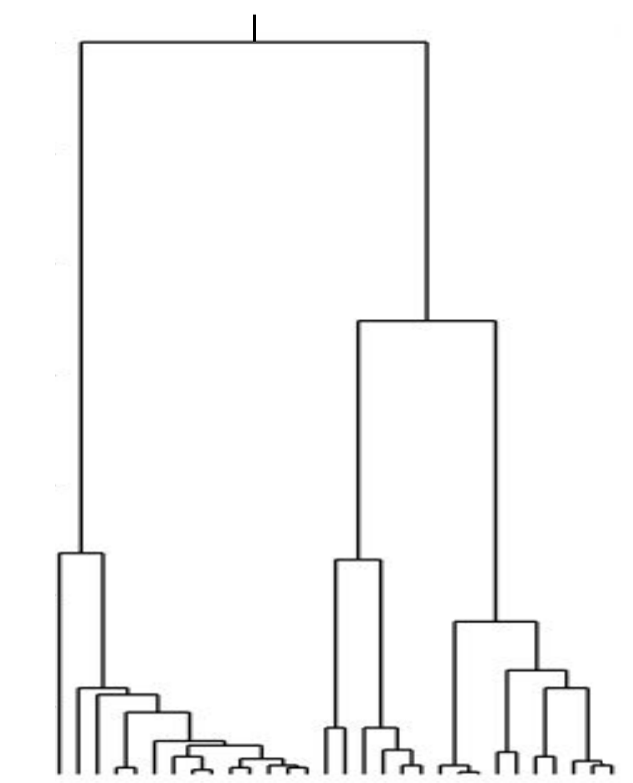
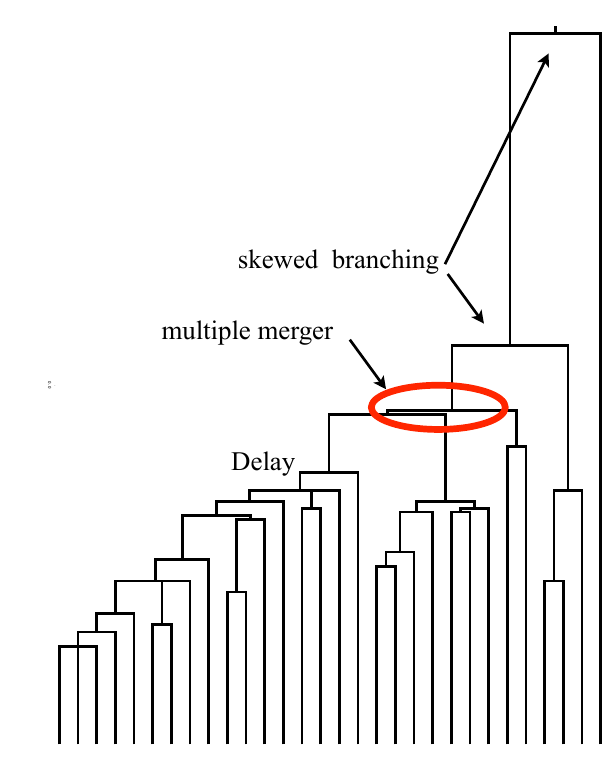
Bolthausen-Sznitman Coalescent
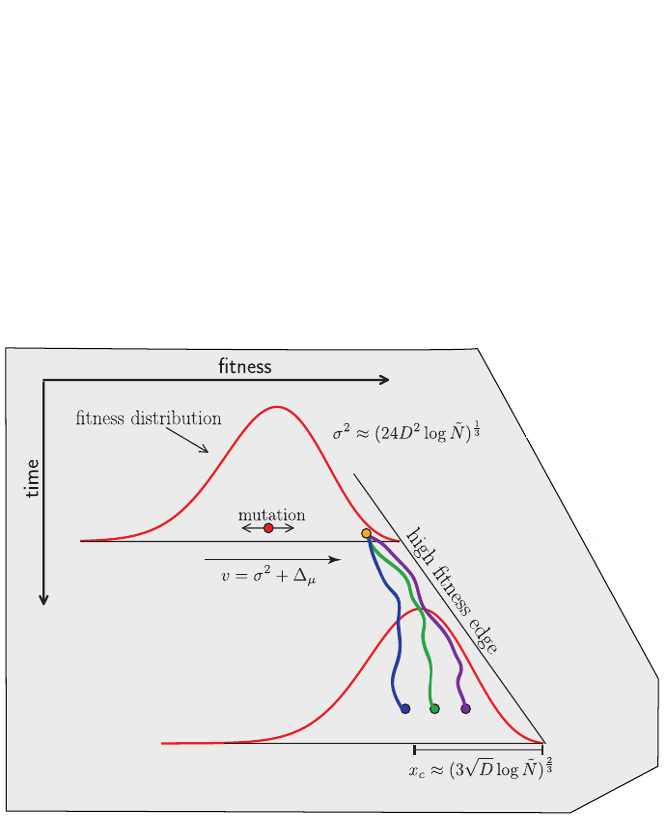
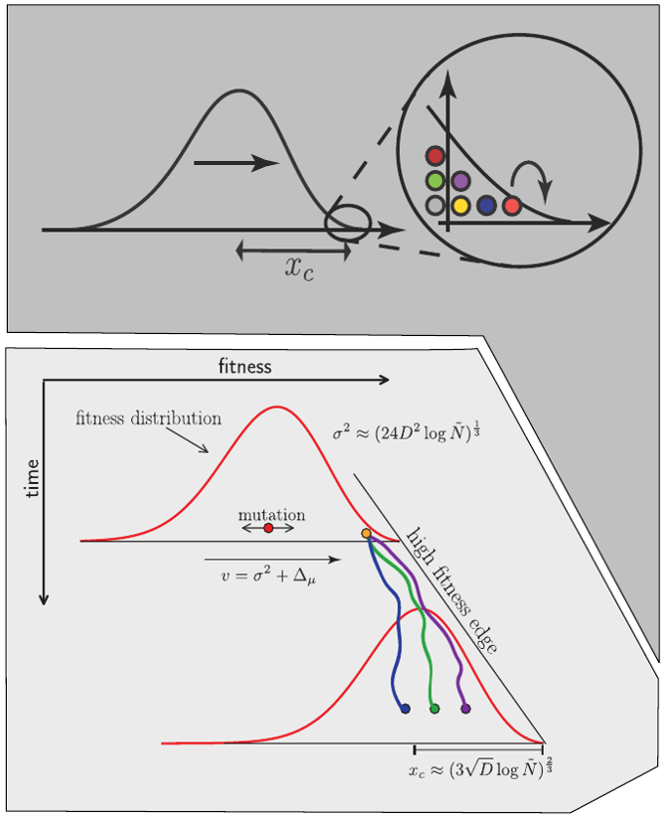
Bursts in a tree ↔ high fitness genotypes
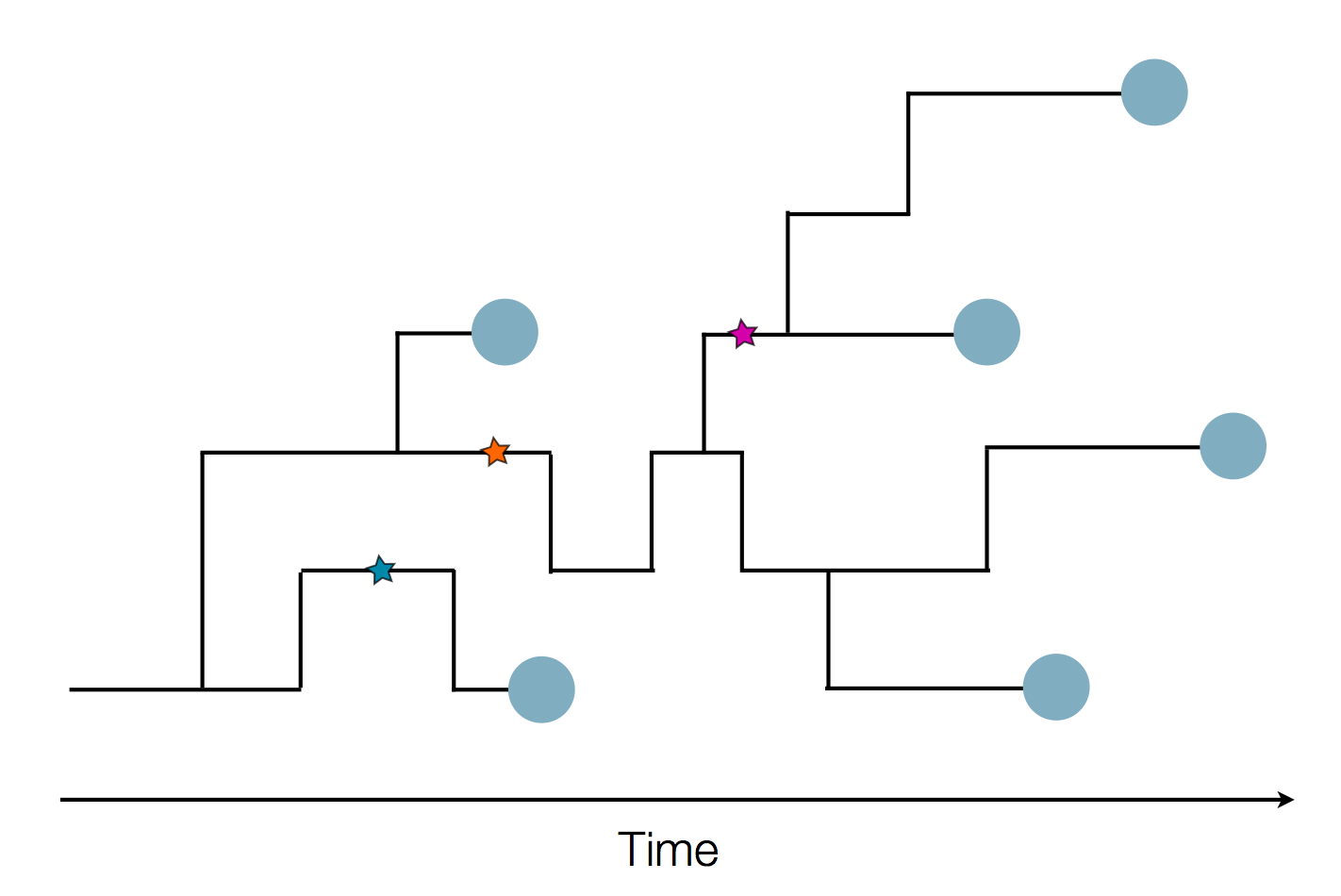
Can we read fitness of a tree?
Predicting evolution
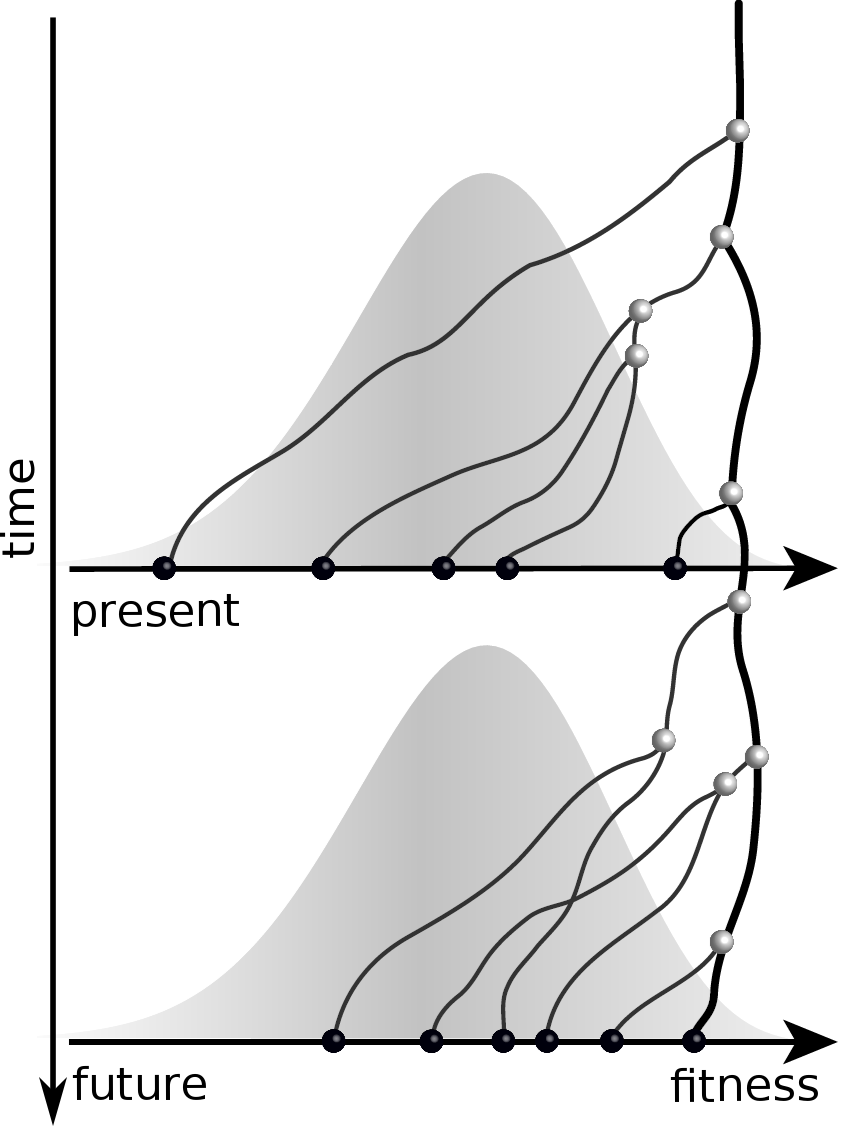
Given the branching pattern:
- can we predict fitness?
- pick the closest relative of the future?
Fitness inference from trees
$$P(\mathbf{x}|T) = \frac{1}{Z(T)} p_0(x_0) \prod_{i=0}^{n_{int}} g(x_{i_1}, t_{i_1}| x_i, t_i)g(x_{i_2}, t_{i_2}| x_i, t_i)$$
RN, Russell, Shraiman, eLife, 2014
Prediction of the dominating H3N2 influenza strain
- no influenza specific input
- how can the model be improved? (see model by Luksza & Laessig)
- what other context might this apply?
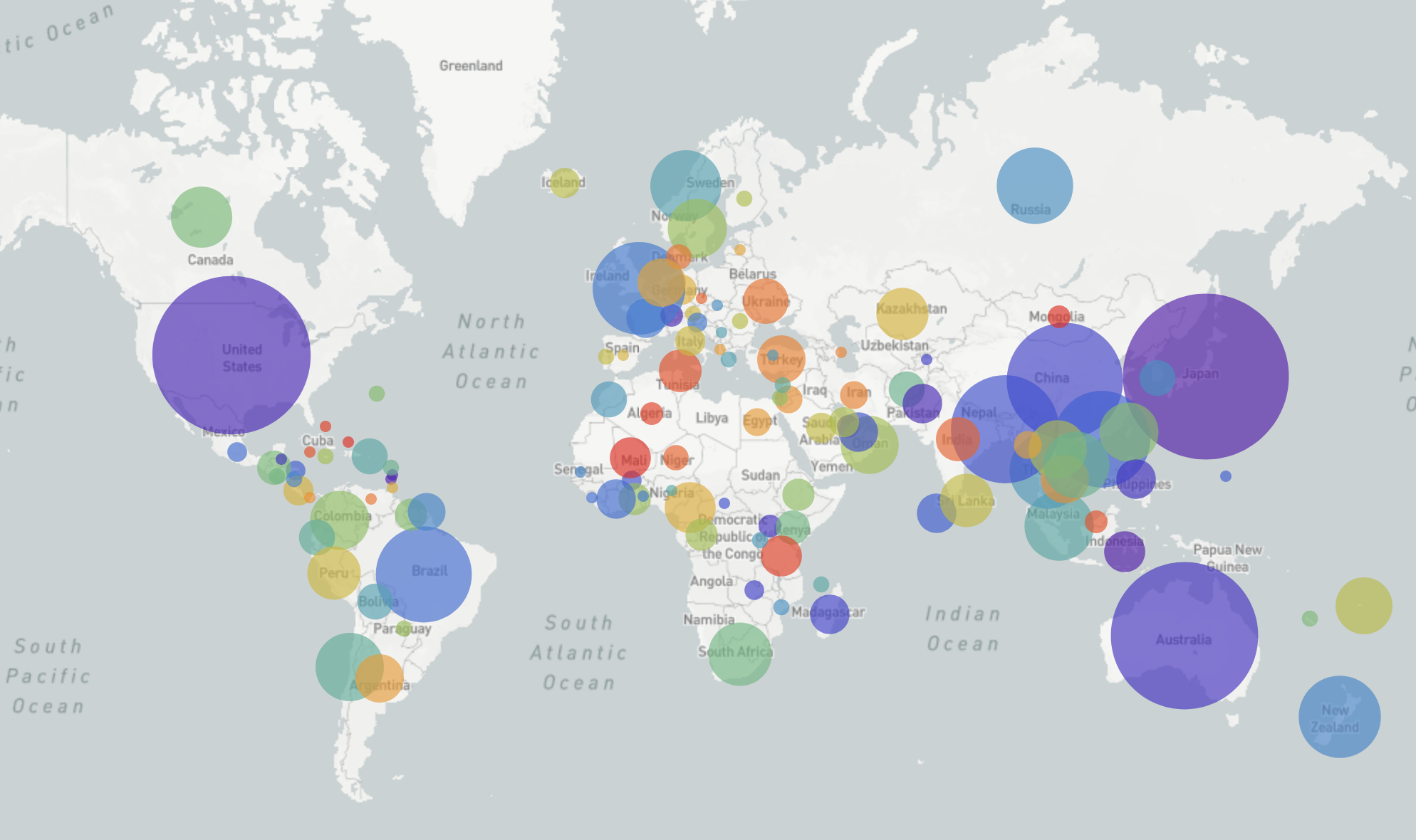
nextstrain.org
joint project with Trevor Bedford & his lab
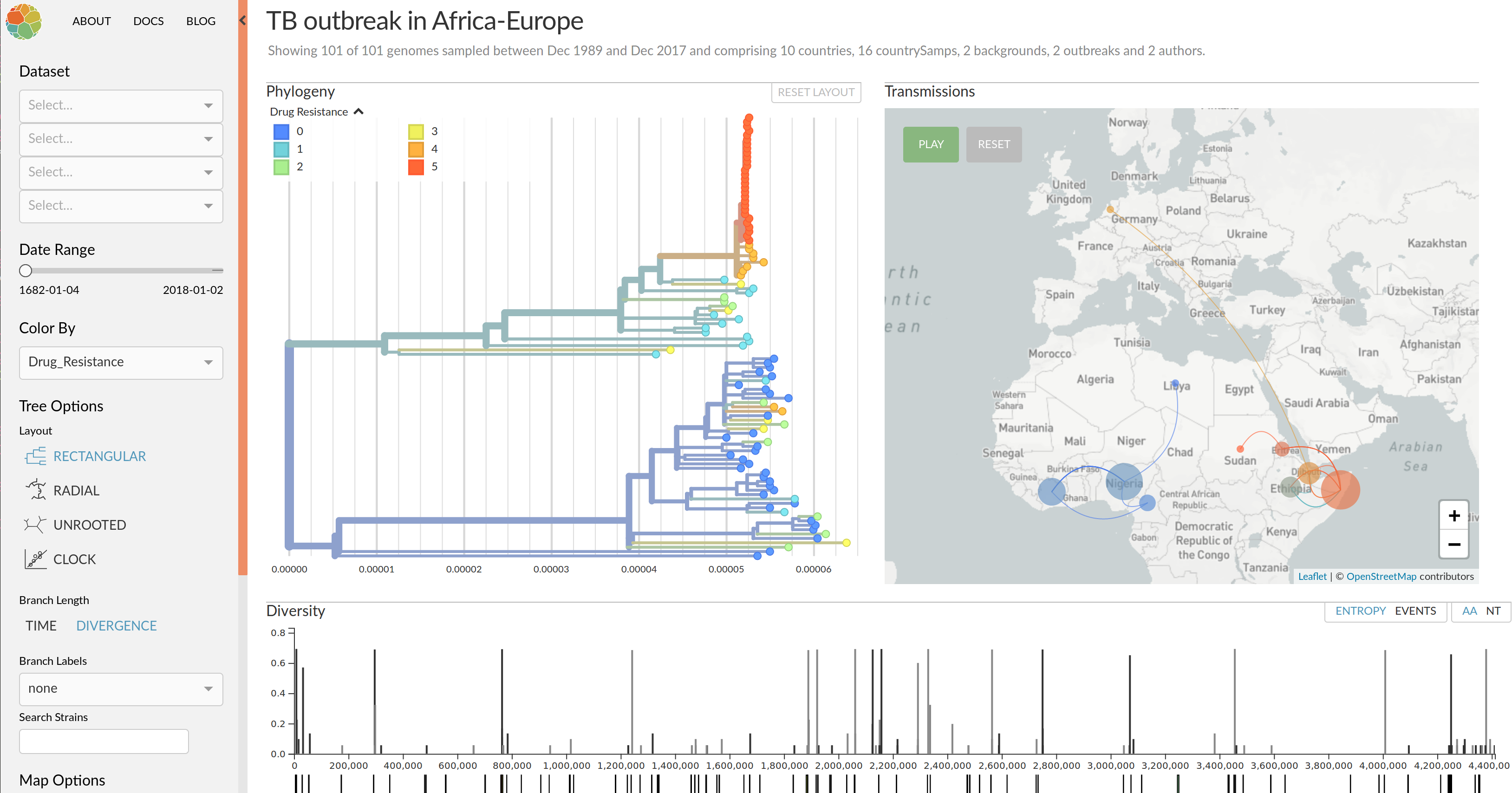

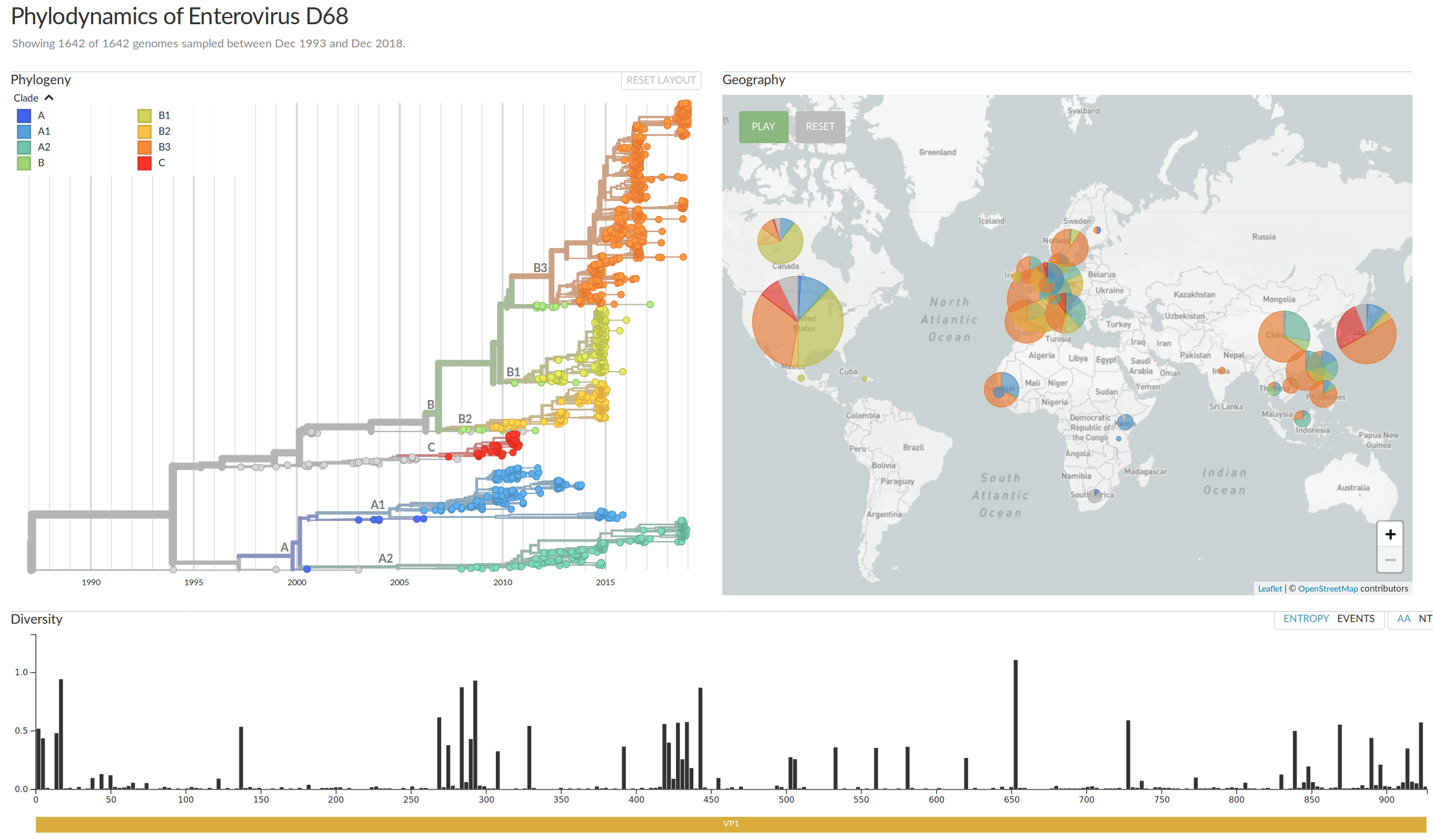
Enterovirus D68 -- with Robert Dyrdak, Emma Hodcroft & Jan Albert
- Non-polio enterovirus
- Almost everybody has antibodies against EV-D68
- Large outbreak in 2014 with severe neurological symptoms in
young children (acute flaccid myelitis) - Another outbreak in 2016
- Outbreaks tend to start in late summer/fall
- Several reports of EV-D68 outbreaks last fall
(201 AFM cases in the US in 2018)
EV-D68 whole genome deep sequencing project across Europe
Infections with multiple variants
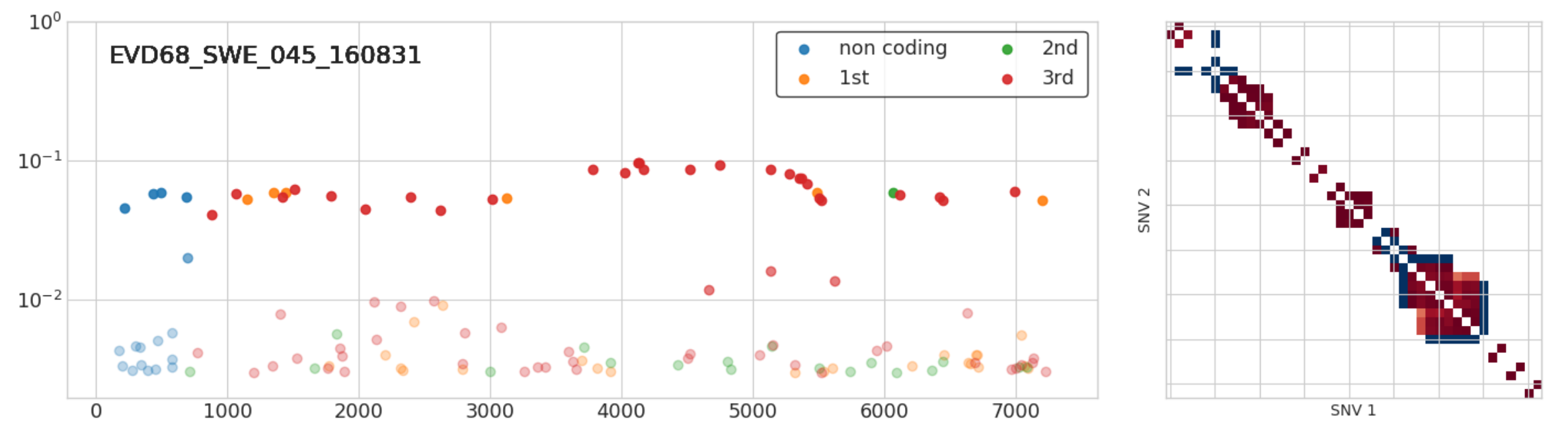
- A set of iSNVs at very similar frequencies in full linkage
- Suggest infection with two related variants
- 3 out of 50 samples: Implies high prevalence
Carbapenemase producing bacteria
- Reserve antibiotics used to treat MDR bacteria
- Introduced in the 1980ies
- Resistance spread rapidly
- Resistance is mediated by several distinct beta-lactamases
→ pressing public health problem
→ fascinating instance of genes sweeping the globe by horizontal transfer
- Resistance is horizontally acquired
→ tracking the core genome doesn't do it - Need to track genes on there mobilizing genetic background
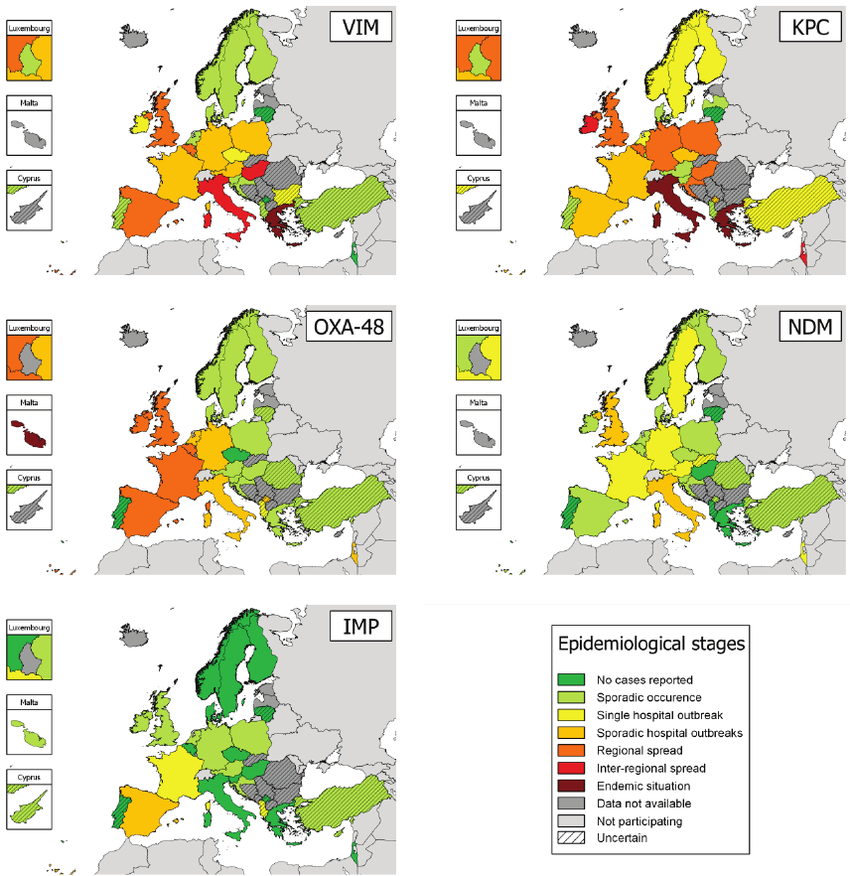
Tracking bacteria by sequencing
- Illumina → millions of short reads (<500bp)
- Too short to bridge repetitive elements
- → assemblies are fragmented into 100s of "contigs"
- Problem: all the important bits are flanked by repetitive/mobile elements

(really terrible example)
Long-read sequencing
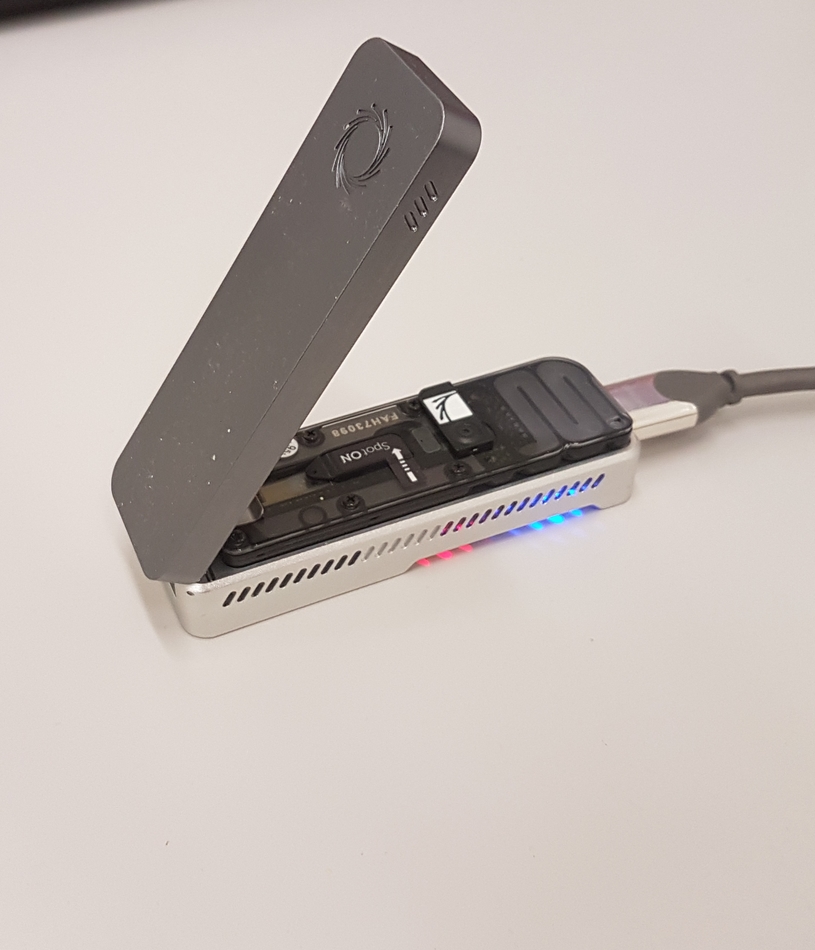



Long-read sequencing of Carbapenemase producing bacteria
- Contigs with drug resistance genes ~1-6 genes
→ no phylogenetic resolution - long-read assemblies give full length plasmids
- tracking via synteny and structural diversity, not SNPs
→ we need to reconstruct spread from genome structure evolution
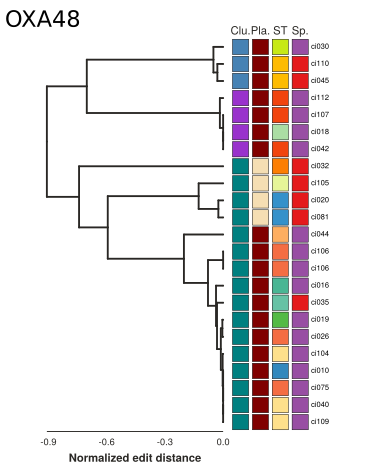
Synteny alignments of Carbapenemase containing loci
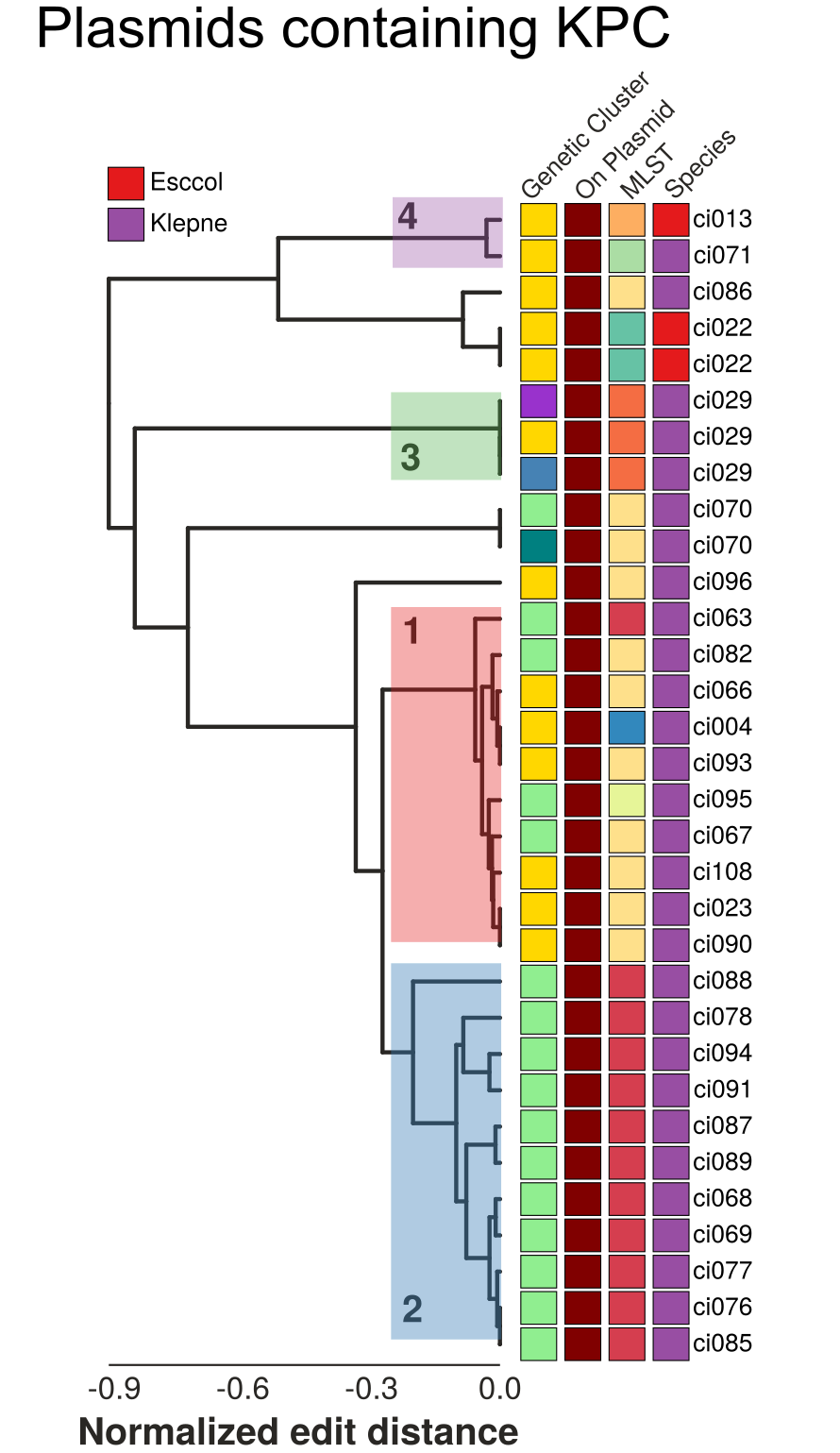
- Structural changes can resolve evolutionary relationships
- Different KPC alleles are found on the same background
- Identical KPC alleles are found on different backgrounds
- Similar plasmids are spread across MLSTs and species boundaries
Synteny alignments of Carbapenemase containing loci


Summary
- Timely data sharing + automated analysis allows near real-time tracking of influenza
- Such analyses provide important input for vaccine strain selection
- Sequencing, analysis, and dissemination can be rapidly set-up for emerging pathogens
- Bacterial pathogens come with a special set of challenges
- Fascinating evolutionary process beyond mutations in homologous sequence
Acknowledgments -- nextstrain






- Trevor Bedford
- Colin Megill
- Pavel Sagulenko
- Sidney Bell
- James Hadfield
- Wei Ding
- Emma Hodcroft
- Sanda Dejanic
- John Huddleston
- Barney Potter




Influenza and Theory acknowledgments




- Boris Shraiman
- Colin Russell
- Trevor Bedford
- Oskar Hallatschek



Acknowledgments -- Enterovirus
- Robert Dyrdak
- Jan Albert
- Lina Thebo
- Emma Hodcroft
- Bert Niesters (Groningen)
- Randy Poelman (Groningen)
- Elke Wollants (Leuven)
- Adrian Egli (Basel)
- Andrés Antón Pagarolas (Barcelona)

Acknowledgments -- CPE
- Wei Ding
- Nicholas Noll
- Eric Ulrich
- Adrian Egli (at USB)

With-in host diversity
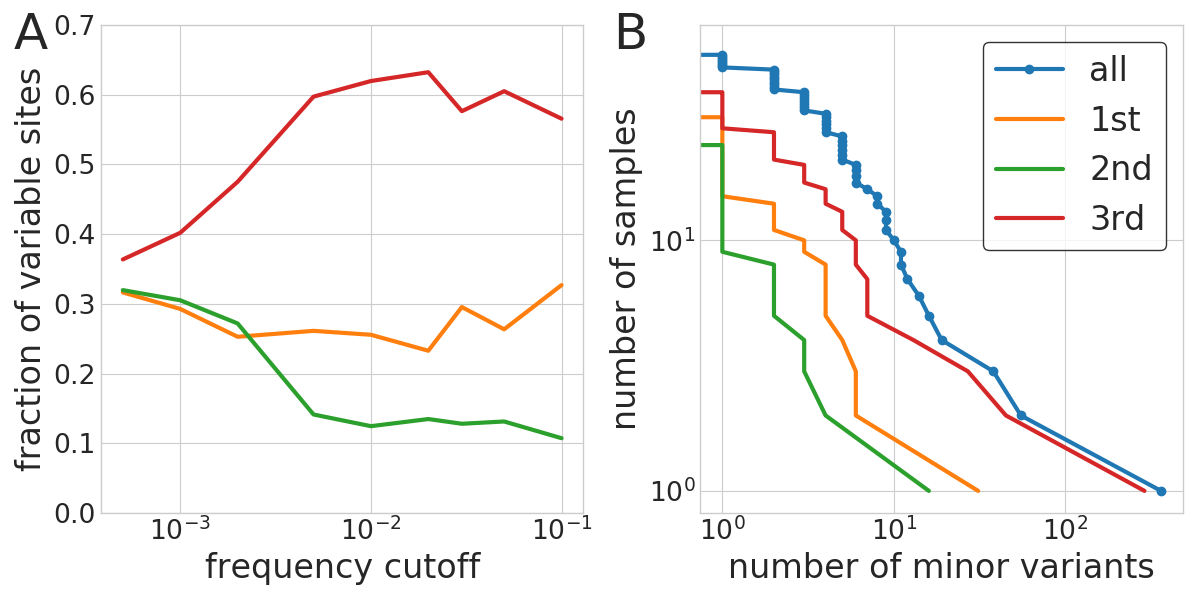
- Above 0.5%, iSNVs are biological
- Most samples have few iSNVs, three had more than 20