Potential impact of seasonal forcing on a SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Richard Neher
Biozentrum, University of Basel
slides at neherlab.org/202005_HIV_Dyn.html
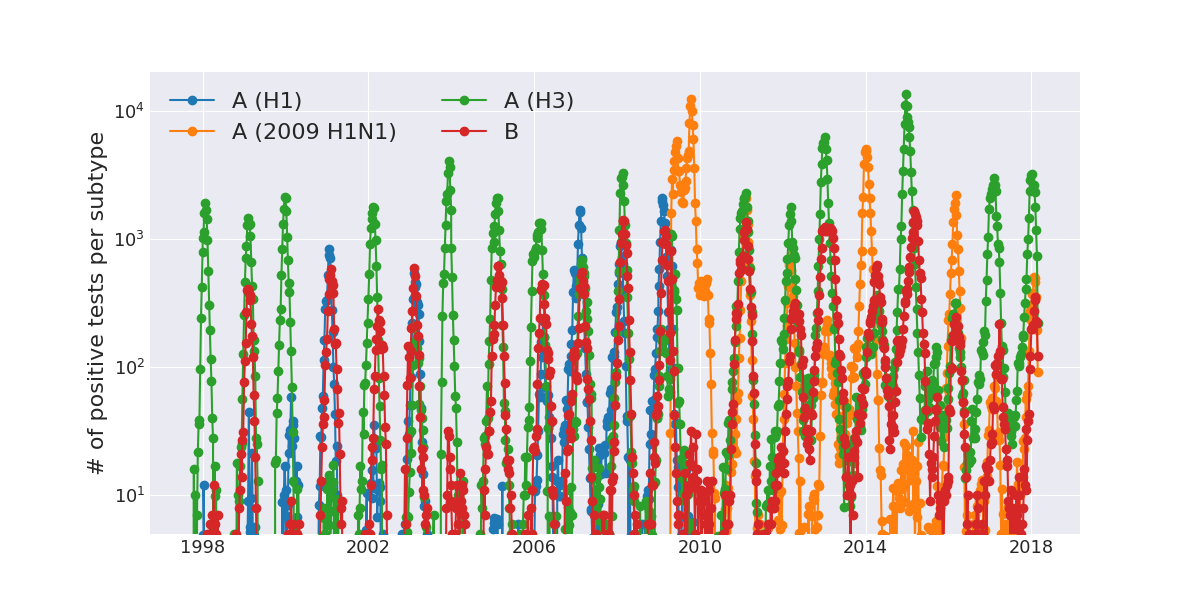
Seasonal incidence of influenza viruses
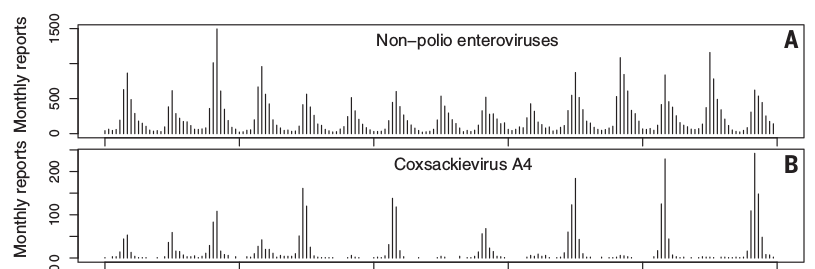
Seasonal incidence of enteroviruses
Potential seasonal drivers
- humidity (e.g. dry air increases time before droplets fall down)
- temperature
- UV light
- behavior (e.g. time spent indoors, ventilation, heating)
Exact nature of forcing not relevant for this talk...
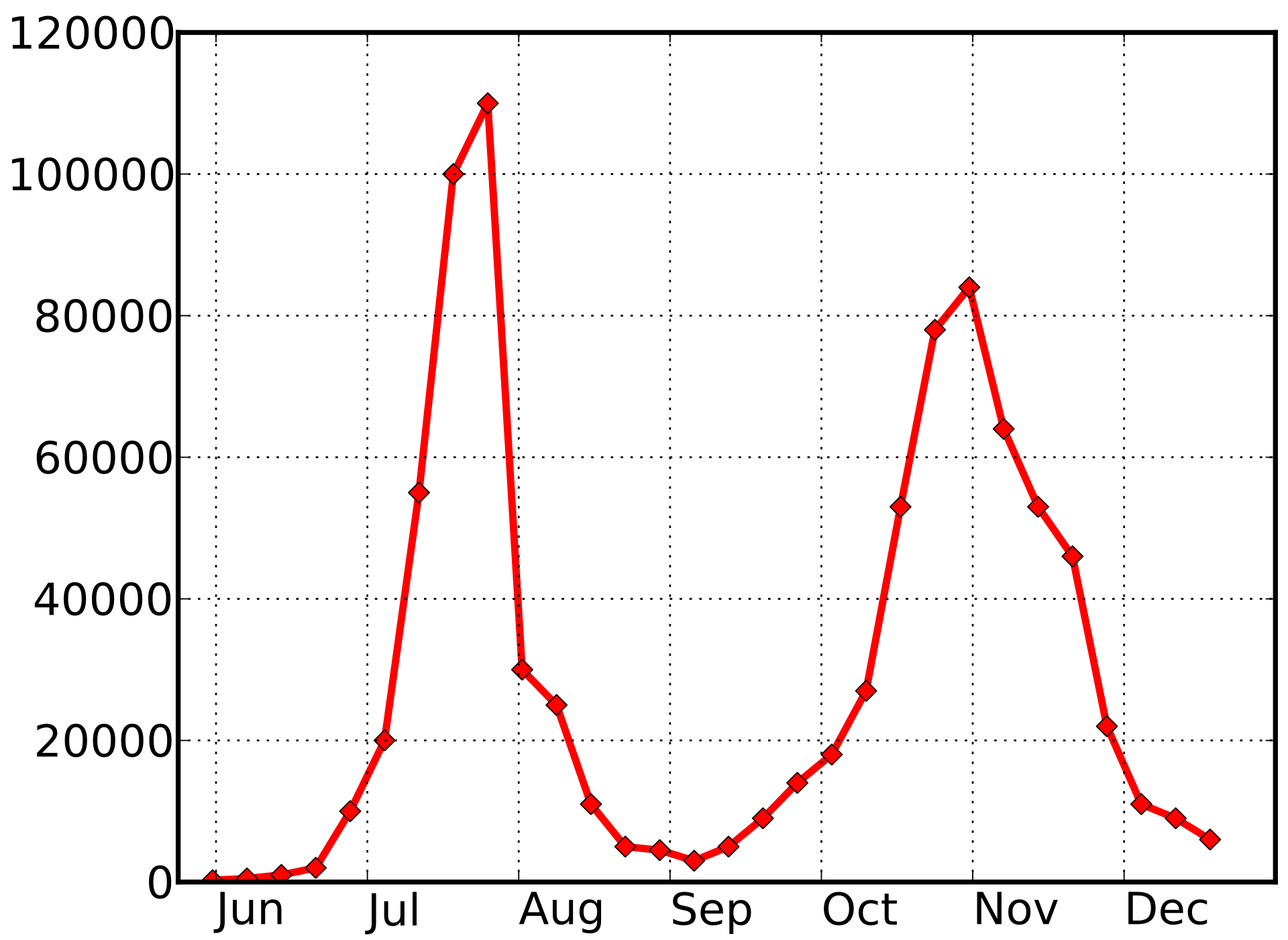
2009 pandemic influenza -- UK
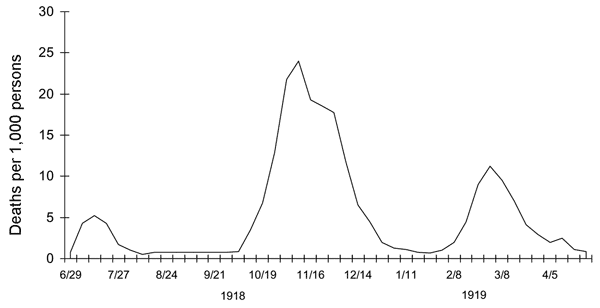
1918 influenza --- UK
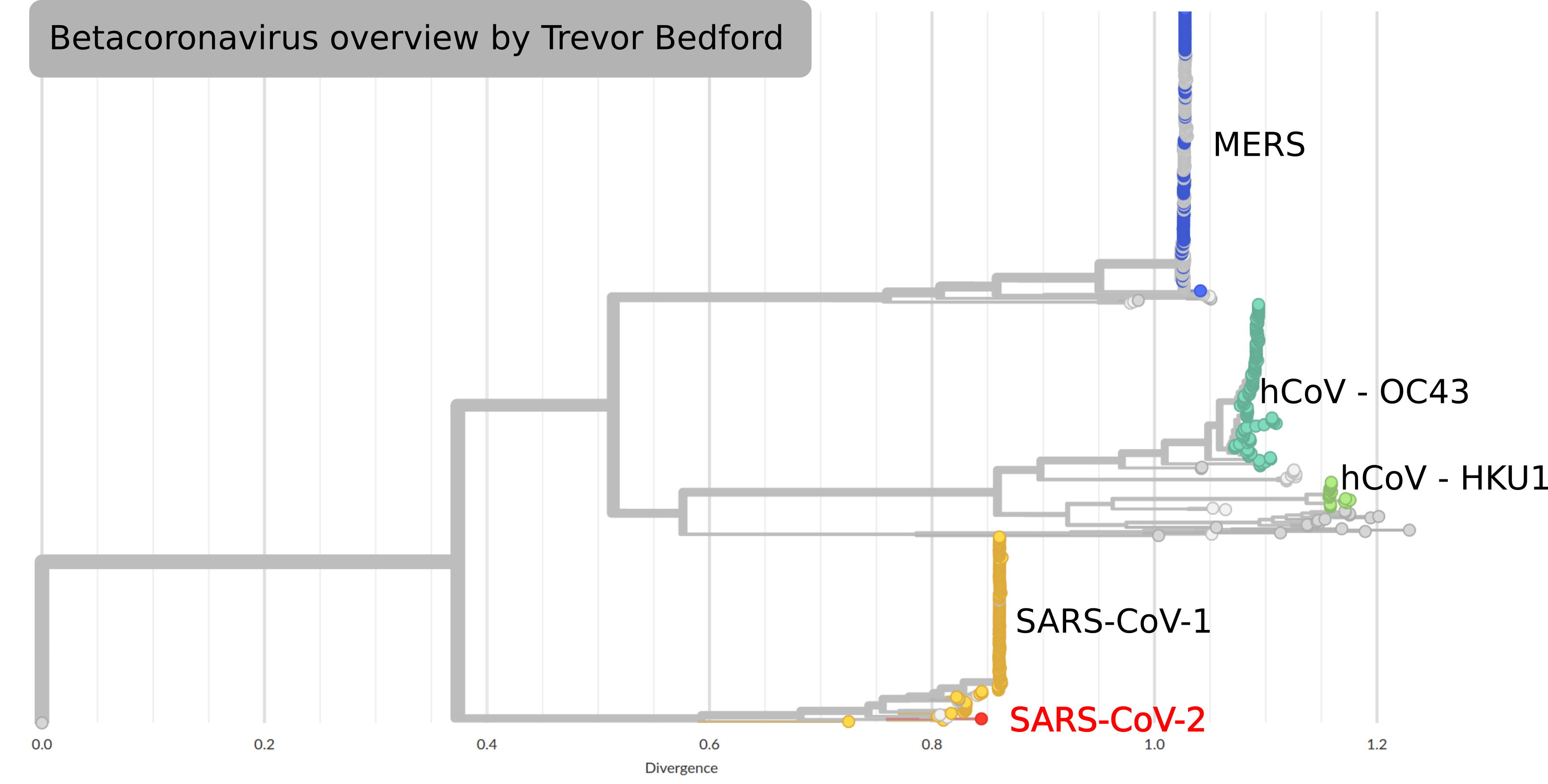 by Trevor Bedford
by Trevor Bedford
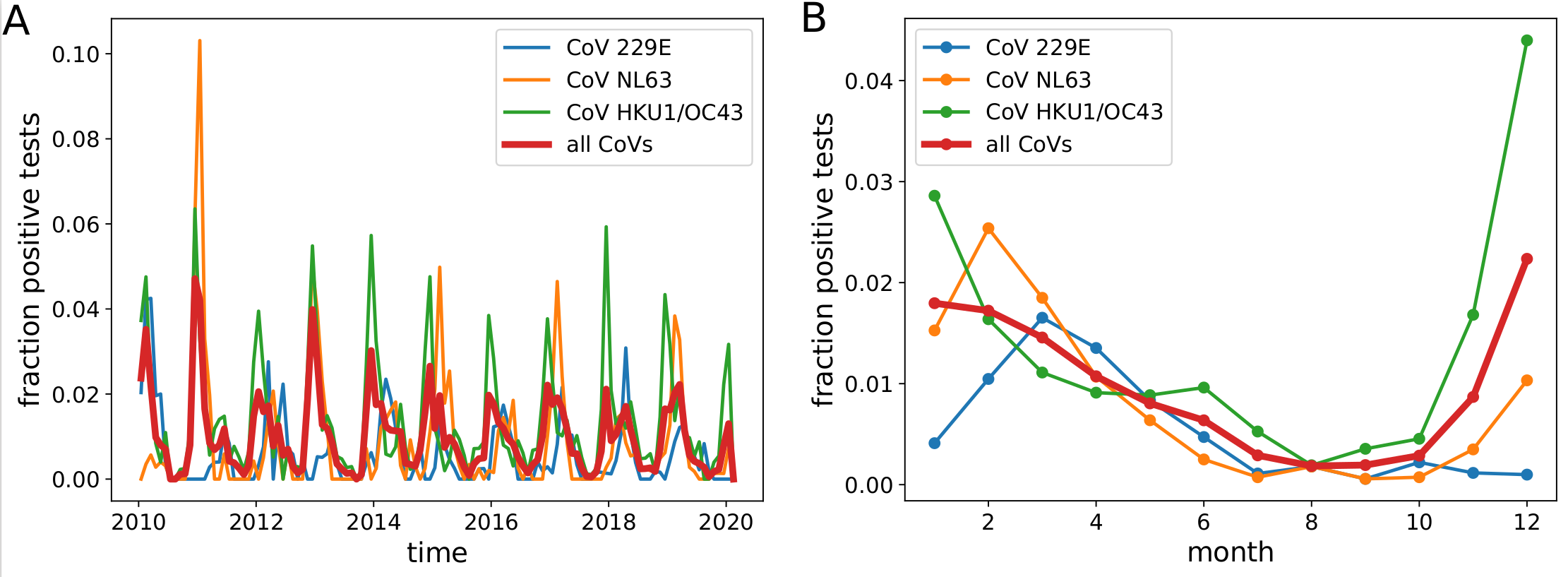
Human corona viruses have pronounced seasonal prevalence (Sweden)
SIR model with seasonal forcing
Strong seasonality can be generated through strong forcing or resonance
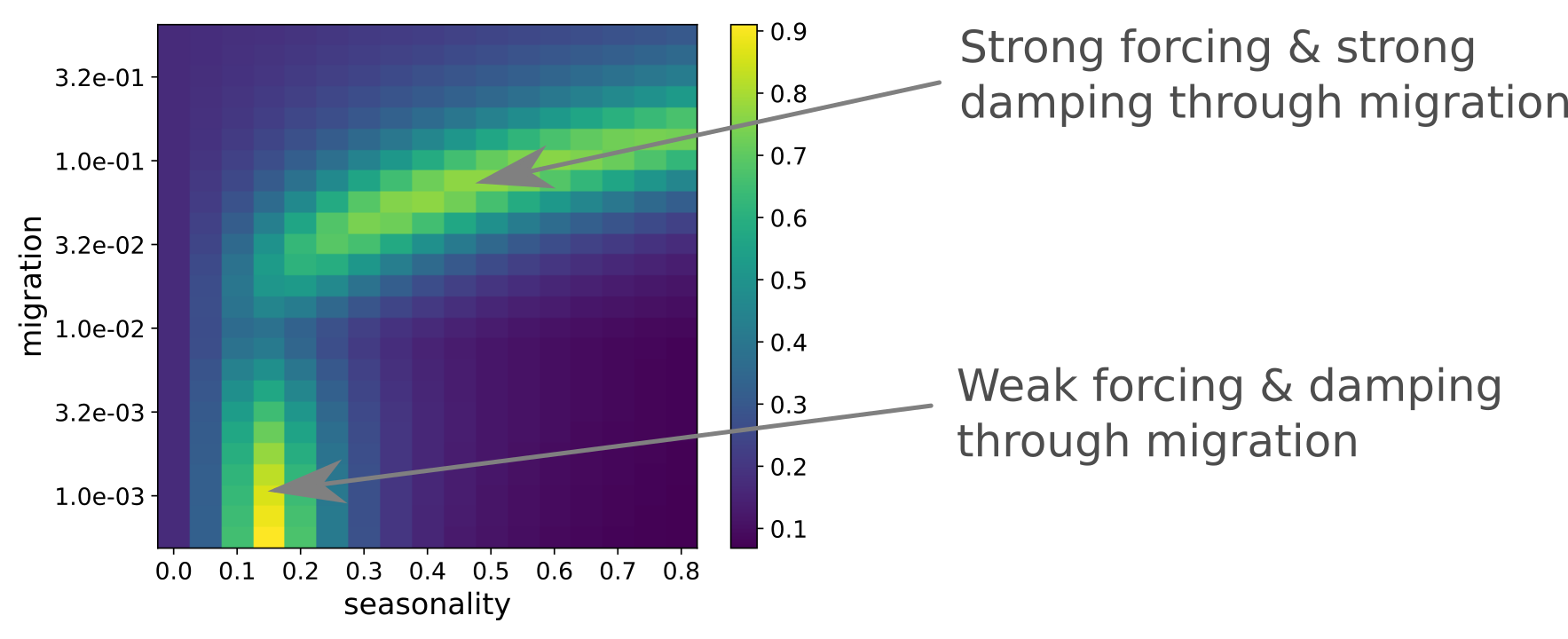
Yellow: good fit -- Blue: poor fit
Seasonal forcing and the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Counter-factual scenario without strong social distancing!
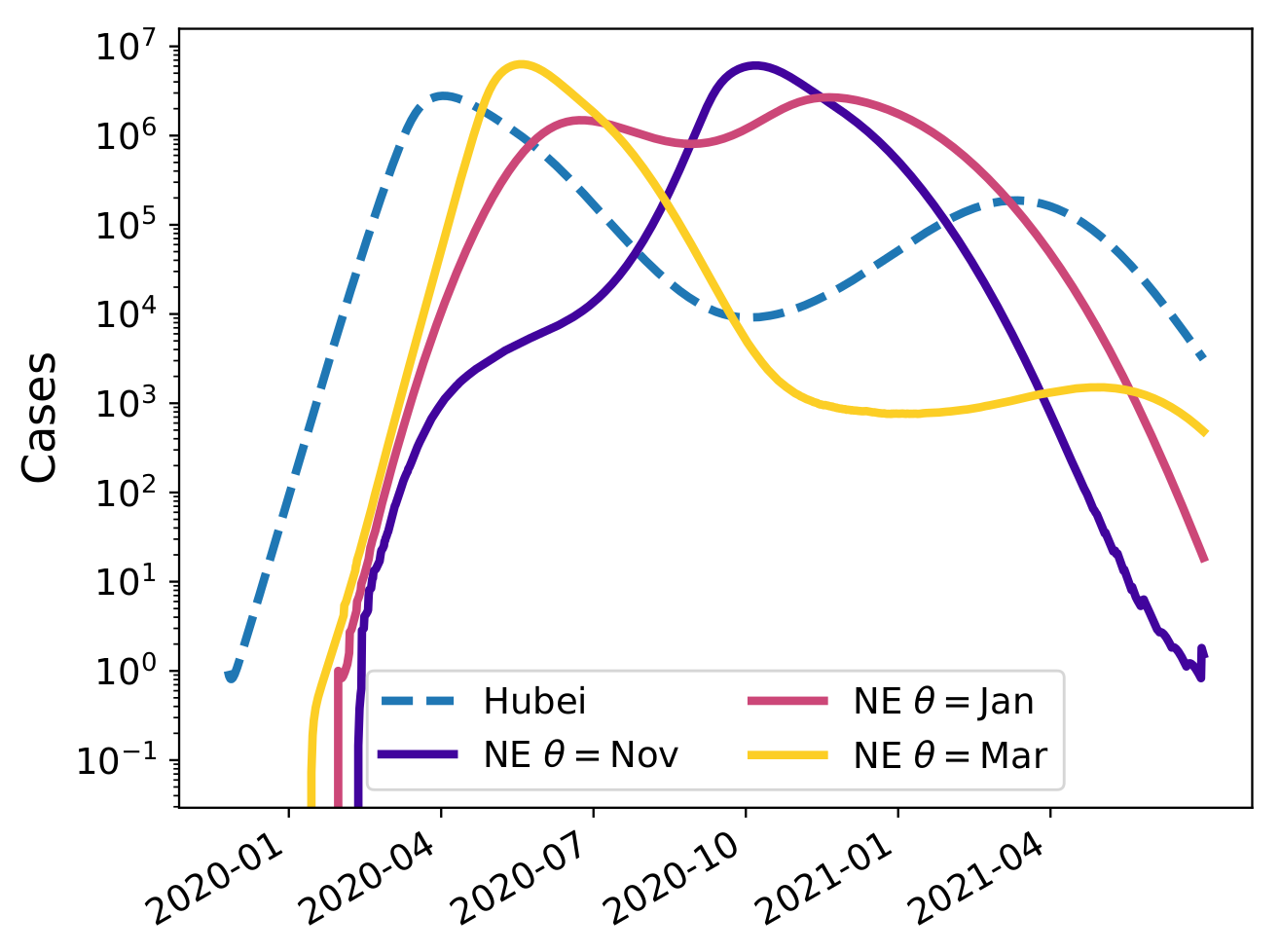
Seasonal forcing and the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
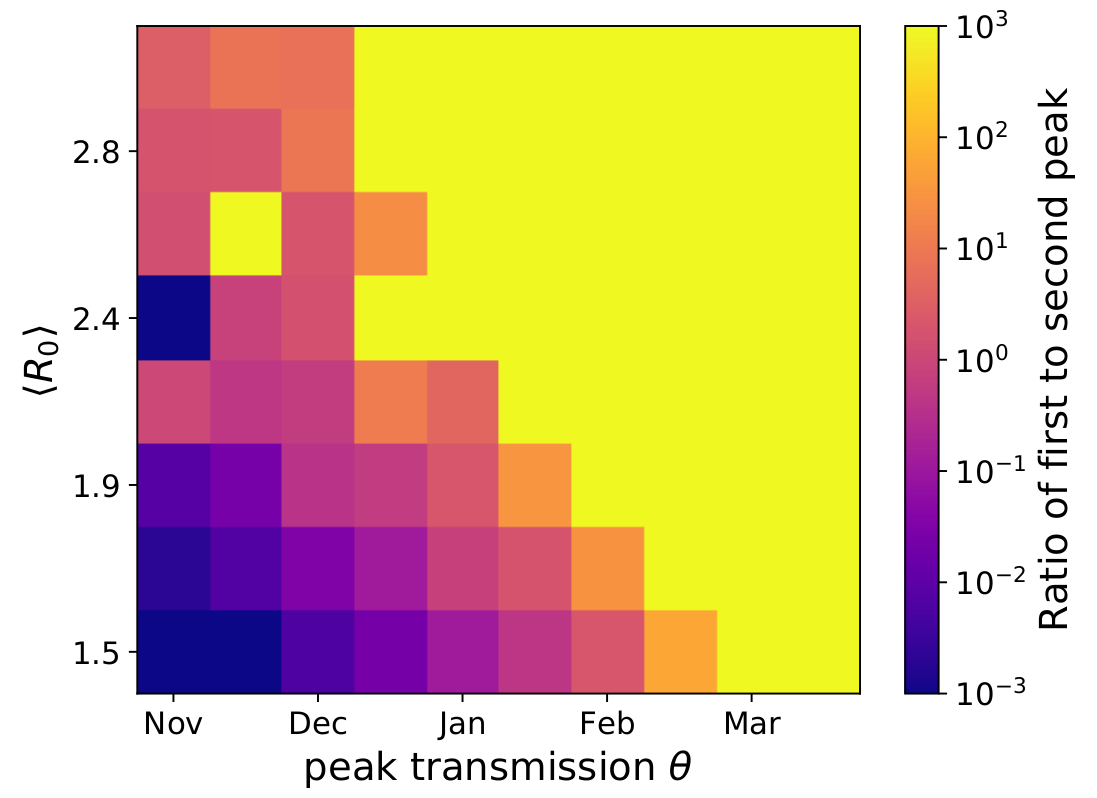
Potential transition to an endemic seasonal virus
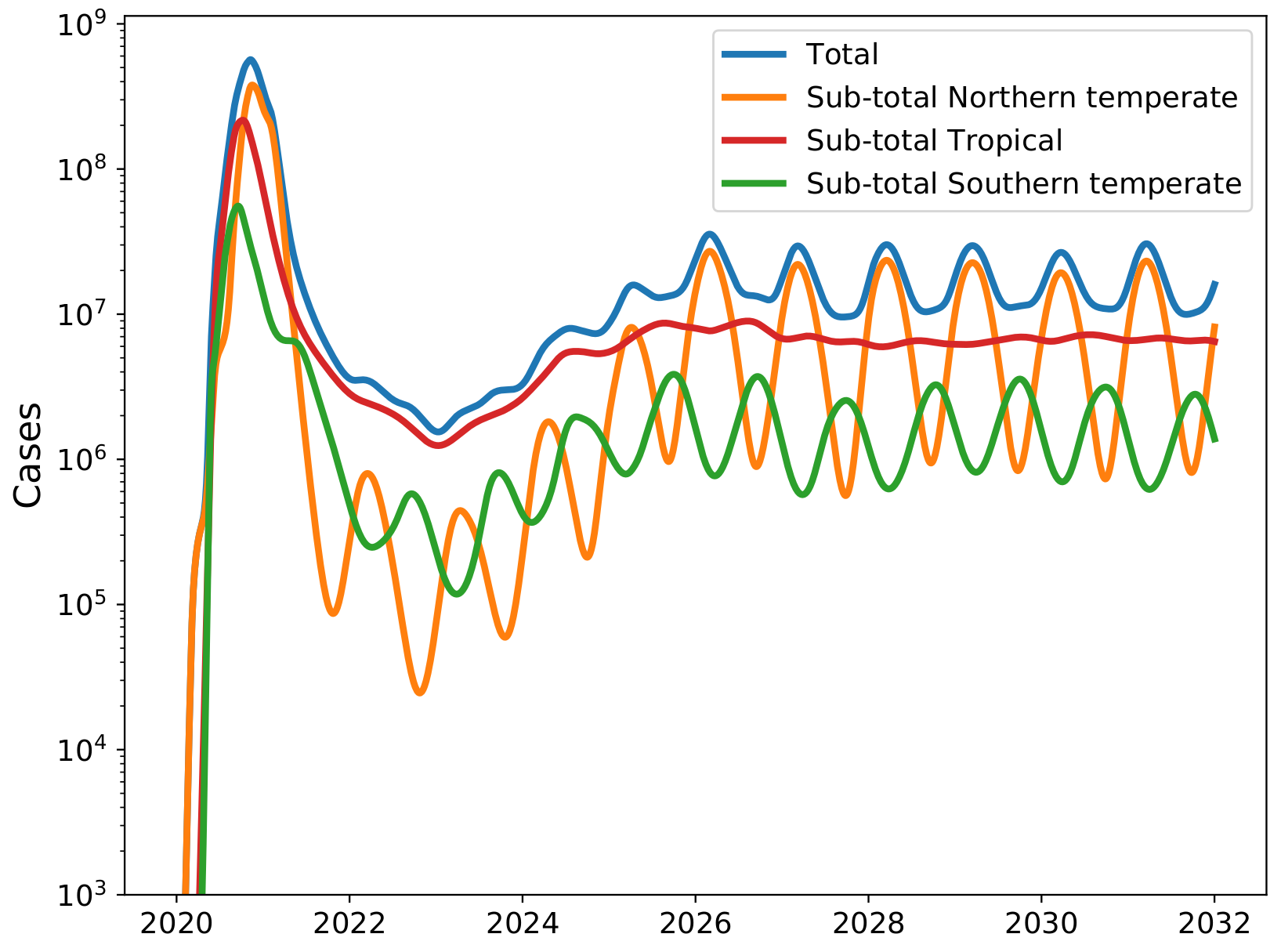
Acknowledgments
- Robert Dyrdak
- Jan Albert
- Valentin Druelle
- Emma Hodcroft


